This white tag identifies wood-burning fireplaces that meet EPA’s Phase 2 emissions levels for the voluntary program. Models that carry this tag have been tested by an EPA-accredited laboratory and are cleaner than other models. You can download full versions of the hang tags at the bottom of this page.
To better understand how your model was rated, click on or place your mouse on the red number on the hang tag graphic to view the definitions.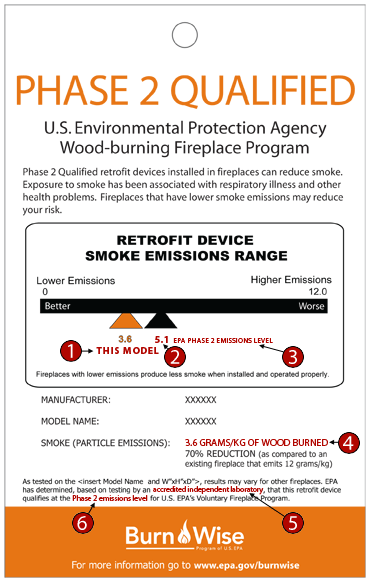
"This Model" Designation - shows the pollution emission level for this particular model. This number resulted from the emissions test used to compare the fireplace with the EPA qualifying emissions level.
"5.1" EPA Phase 2 Emissions Level - the fireplace must meet this level (measured in grams/kilogram of wood burned) to qualify for the EPA Phase 2 voluntary program.
"Phase 2" - is the final step of EPA's phased program to provide better choices of fireplaces that are cleaner and more efficient than unqualified fireplaces.
"Grams/kg of Wood Burned" - shows the amount of particle pollution (measured in grams) per unit of wood burned (measured in kilograms).
"Accredited Independent Laboratory" - These testing labs are third parties that are (1) accredited by a nationally recognized accrediting body to perform testing under ASTM test methods E2558 and E2515 under ISO-IEC Standard 17025, or (2) accredited for wood stove certification testing under the residential wood heater NSPS [40 CFR Part 60, Subpart AAA]. An important criterion is that these labs are independent of the manufacturers. Also, this lab accreditation is determined by reviewing the lab’s performance, the capabilities of performing specific types of testing, and accurately and fully compiling test results. In addition, EPA will receive a Certificate of Conformity for each model by a certification body accredited by a nationally recognized accrediting body to perform certifications and inspections under ISO-IEC Guide 65, and ISO-IEC Standard 17020. A certification body would certify conformity with Program emission levels and perform other functions pertaining to certification (e.g., manufacturing facility inspections).
"Emissions Level" - designated by EPA as a maximum of 5.1 grams/kilogram of wood burned. EPA established this number with input from various stakeholder groups such as industry manufacturers, EPA-accredited testing laboratories, state air quality agencies, the Northeast States for Coordinated Air Use Management (NESCAUM), and the Western States Air Resources Council (WESTAR).
The following are full-sized versions of the fireplace and fireplace retrofit device hang tags:
You may need a PDF reader to view some of the files on this page. See EPA’s About PDF page to learn more.- Fireplace Phase 2 White Hang Tag (PDF)(1 pg, 214 K)
- Retrofit Device Phase 2 Hang Tag (PDF)(1 pg, 221 K)
