Salmon Mapper
“Salmon Mapper” − Pesticide Use Limitations in California, Oregon and Washington State
Background
The "Salmon Mapper" GeoPlatform Application is intended to assist pesticide users' understanding of the spatial extent of certain pesticide use limitations to protect endangered or threatened salmon and steelhead in:
- California;
- Oregon; and
- Washington.
The hydrologic data used in this interactive map application were downloaded from the:
- National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) in California, managed by the U.S Geological Survey (USGS); and
- StreamNet Dataset Exit in Washington and Oregon, managed by the Pacific States Marine Fisheries Commission.
Pesticide users should visit this site prior to the time of pesticide use to determine whether the Court-ordered limitations apply to your use of a specific pesticide.
To determine specific waters and pesticide use limitations that may apply to your use of a pesticide, from the list at the right:
- Select the state in which you intend to apply a pesticide;
- Select the specific pesticide active ingredient you intend to use; and
- Click the "Submit" button.
Questions regarding the "Salmon Mapper" may be submitted by email to EPA's Endangered Species mailbox.
On August 15, 2014, in NCAP v. EPA, the United States District Court for the Western District of Washington issued a stipulated injunction reinstating the streamside no-spray buffer zones to protect endangered or threatened salmon and steelhead that were originally imposed in 2004 by the same court in Washington Toxics Coalition (WTC) v. EPA. These buffer zones apply to:
- carbaryl;
- chlorpyrifos;
- diazinon;
- malathion; and
- methomyl.
These court-ordered no-spray buffers, which are not included as labeling requirements under FIFRA, apply to specific waters and specific pesticides’ uses in Washington, Oregon and California. The buffers extend:
- 20 yards from salmon-supporting waters for ground applications of these pesticides; and
- 100 yards for aerial applications.
The stipulated injunction requires EPA to provide on its website maps that identify where the buffers apply. The Salmon Mapper application is designed to satisfy that obligation.
Under the stipulated injunction there are three relevant use exemptions:
- Public health vector control administered by public entities, such as the use of malathion by local governments for mosquito control.
- National Marine Fisheries Service-authorized programs (i.e., where a NMFS finding or permit allows use within the buffers).
- Use of carbaryl under a Washington State-issued 24(c) registration for oyster beds in the estuarine mudflats of Willapa Bay and Grays Harbor.*
*In January 2014, Washington state cancelled use of the Special Local Need (SLN) or 24(c) for carbaryl to control burrowing shrimp. As a result, there is no longer a carbaryl product available for use under this exemption.
The “Salmon Mapper” also includes limitations for the remaining pesticides that were part of the initial 2004 WTC settlement:
- 1,3-dichloropropene;
- bromoxynil;
- metolachlor; and
- prometryn.
EPA will update this site when the Court-ordered limitations change because:
- EPA has implemented any necessary protections for Pacific salmon and steelhead based on reinitiated consultations with NMFS for:
- carbaryl;
- chlorpyrifos;
- diazinon;
- malathion; and
- methomyl; or
- NMFS has completed a final Biological Opinion for:
- 1,3-dichloropropene;
- bromoxynil;
- metolachlor; and
- prometryn.
Online Help
The "Salmon Mapper" application provides users with interactive Geographic Information System (GIS) functionality using spatial data from a variety of sources. The hydrologic data used in this interactive map application were downloaded from the:
- National Hydrography Dataset (NHD) in California, managed by the U.S Geological Survey (USGS); and
- StreamNet dataset in Washington and Oregon, managed by the Pacific States Marine Fisheries Commission.
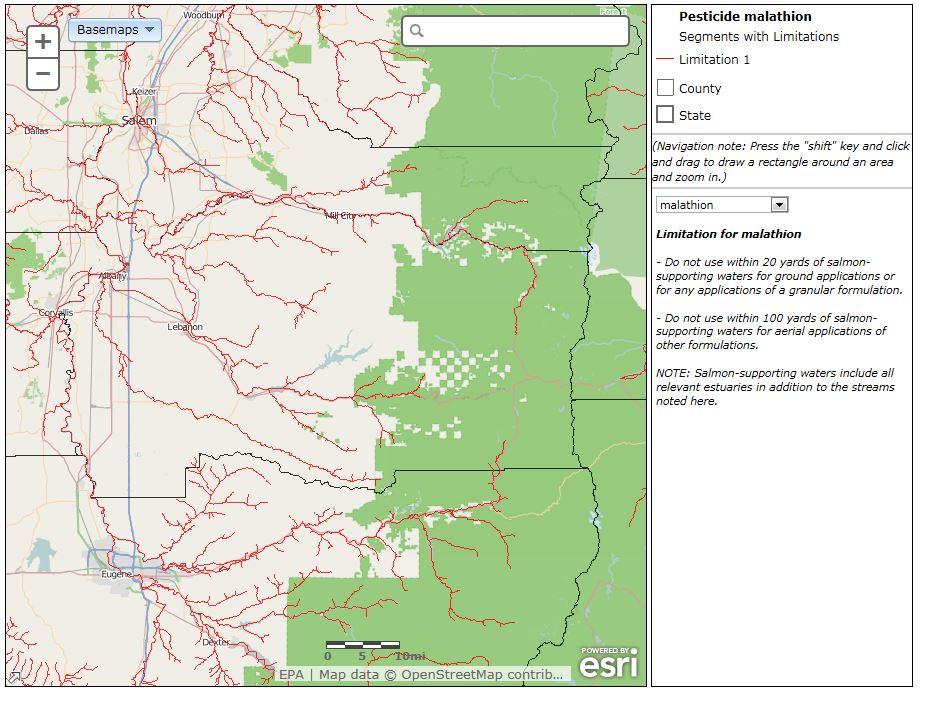
The application allows users to view spatial data for any county in Washington, Oregon or California. A detailed map of rivers and streams for the selected location is created, with those rivers or streams containing limitations on use of designated pesticides in red. The displayed map can be manipulated and changed by zooming in and out, displaying an overview map and changing the background map to show landscape features, streets, etc.
This Online Help module provides additional information on specific features of the “Salmon Mapper” application.
Select Pesticide
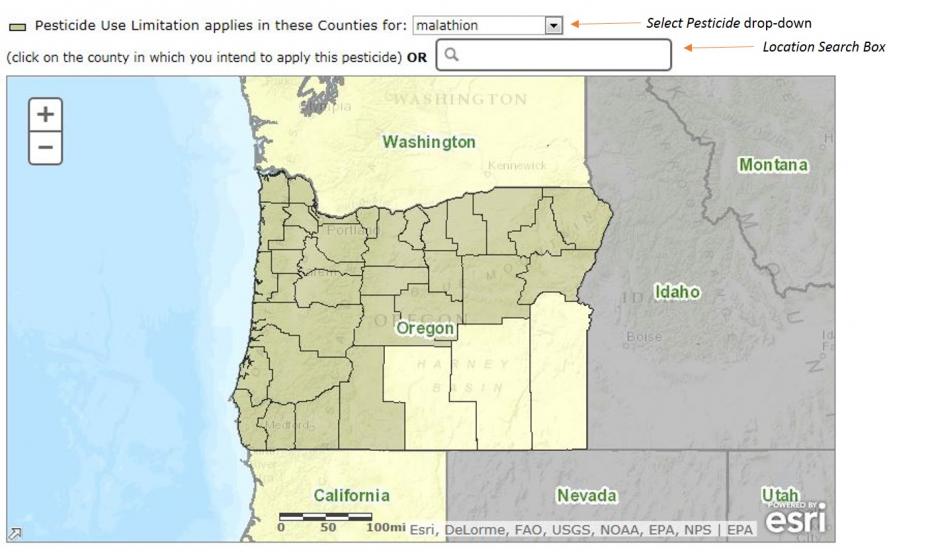
To determine specific waters and usage limitations that may apply to a particular pesticide, choose a state and the specific pesticide active ingredient you intend to use. Then, click the "Submit" button.
Counties in which court-ordered limitations are imposed on streams for the selected pesticide are shaded. You can either click on a county to get information on Pesticide Use Limitations for stream segments found in that county or enter the county name or specific location into the “Location Search Box” to highlight the counties in which limitations for the selected pesticide have been imposed.
When using the "Location Search Box," entering state-specific information with your desired search criteria is critical for the auto-zoom to find the correct location. Names of counties, towns, and landmarks often are repeated across the country. Examples of search criteria include:
- city (Seattle, WA);
- county (King County, WA);
- landmark (Space Needle, WA);
- zip code (zip code 98109); or
- full address (400 Broad St., Seattle, Washington 98109).
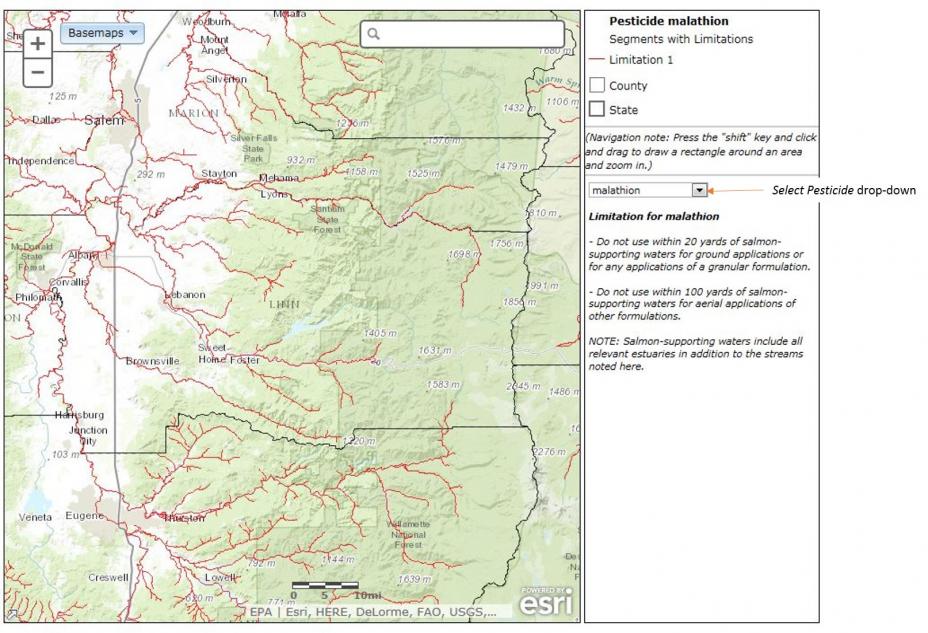
You can change the pesticide using the “Select Pesticides” drop-down menu (located on top of the state map).
Once in the interactive mapper, you can use the “Select Pesticides” drop-down menu (located next to the map in the middle right corner) to redraw the map based upon use limitation information imposed for each pesticide on waters in the map extent. The map will display water segments pertinent for the selected pesticide
Viewing Options
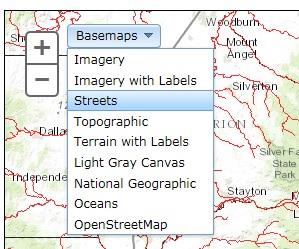
Your background map options include Imagery, Imagery with Labels, Streets, Topographic, Terrain with Labels, Light Gray Canvas, National Geographic, Oceans and OpenStreetMaps. Below are examples of each of these backgrounds.
- Basemaps - Change Background
The basemap tool allows you to change the background of the map.
- Imagery Basemap
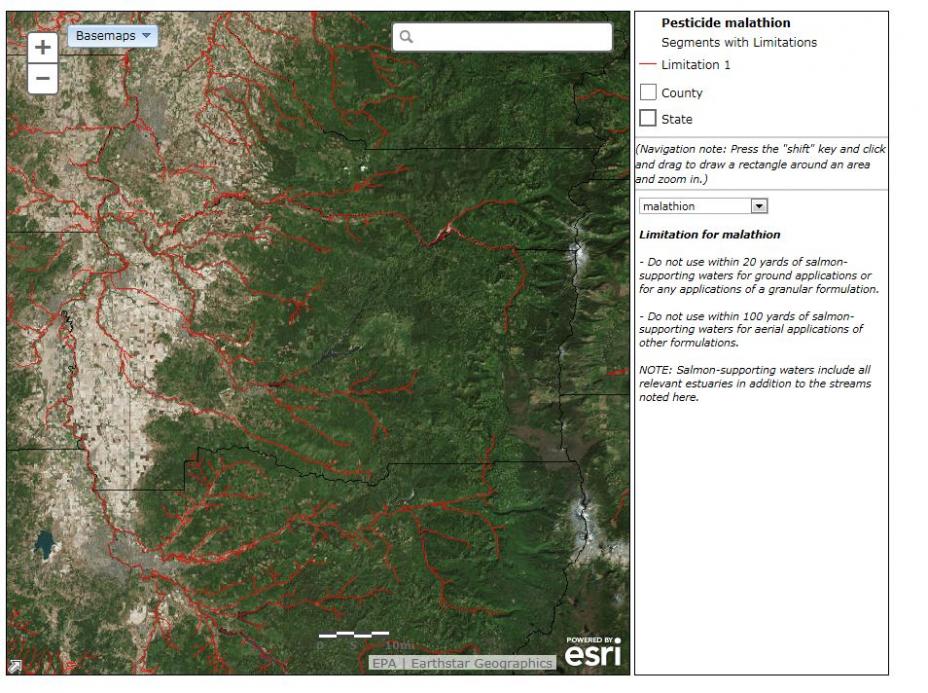
- Imagery Basemap with Labels
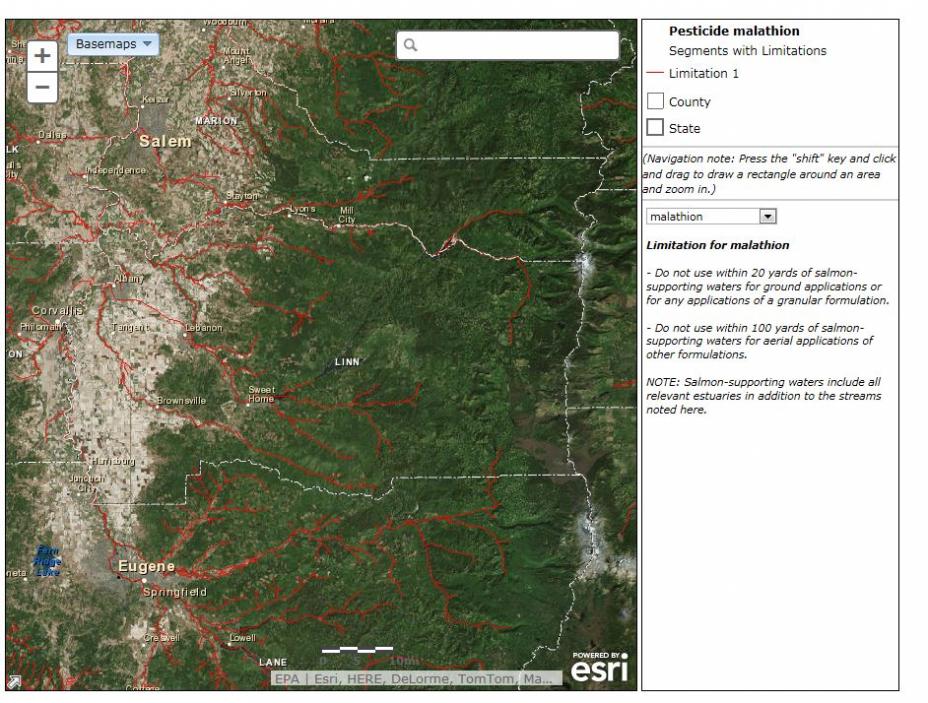
- Streets
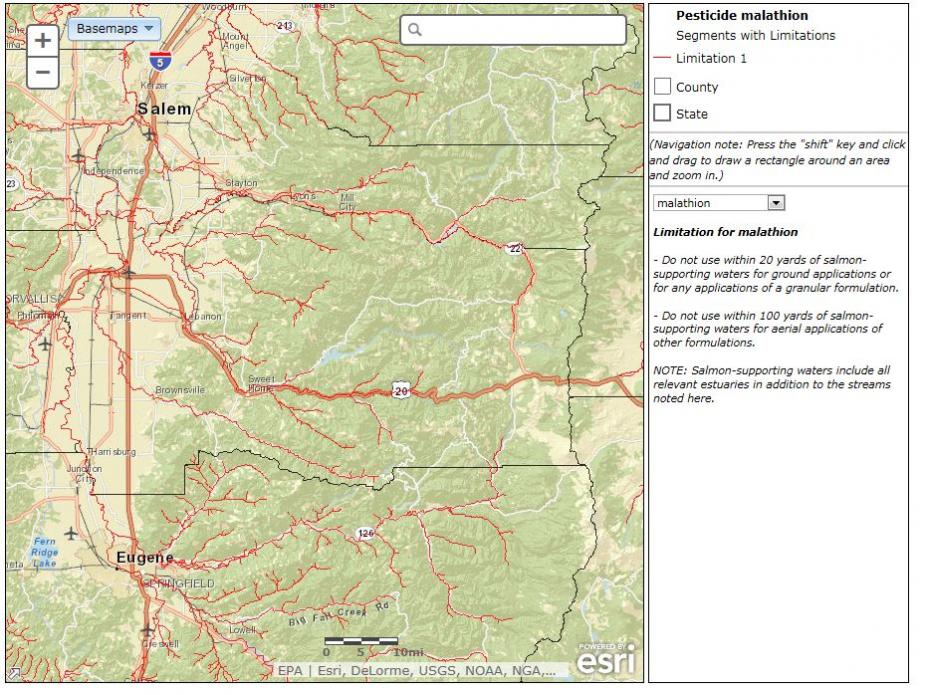
- Topographic (Default Background)
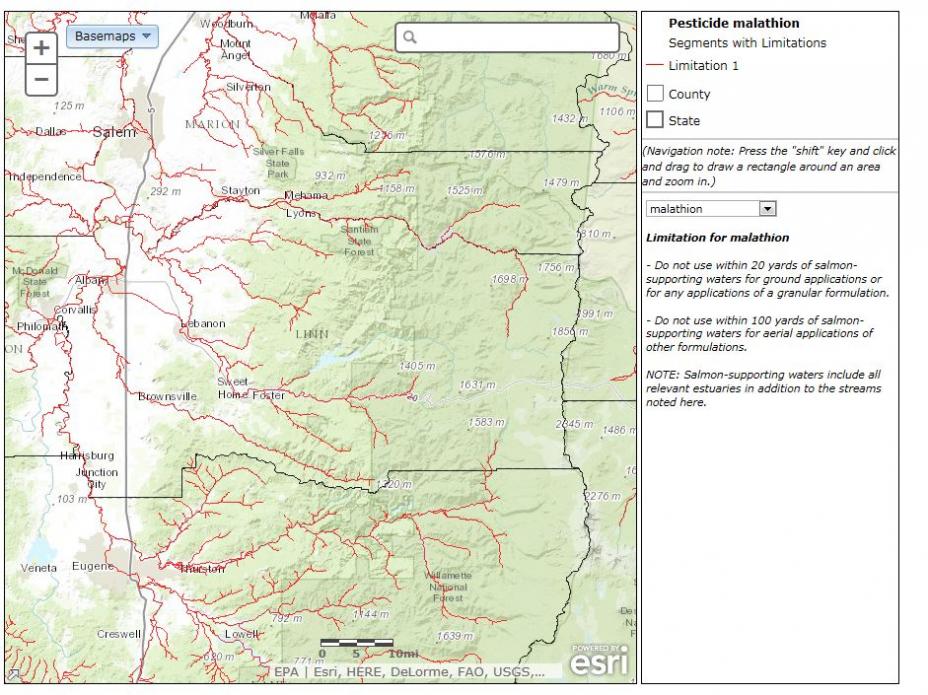
- Terrain with Labels
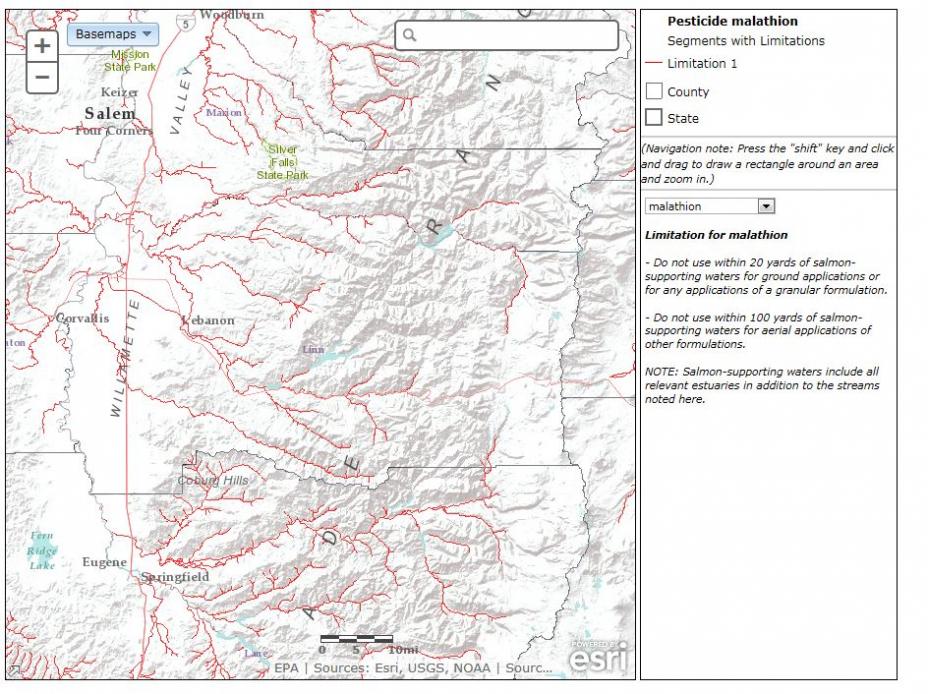
- Light Gray Canvas
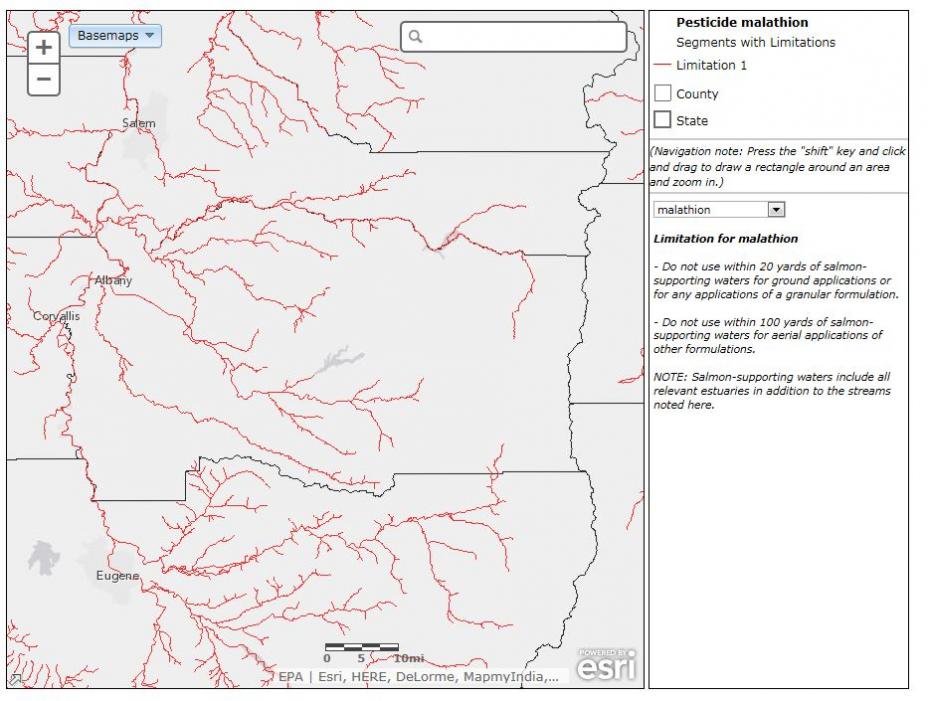
- National Geographic
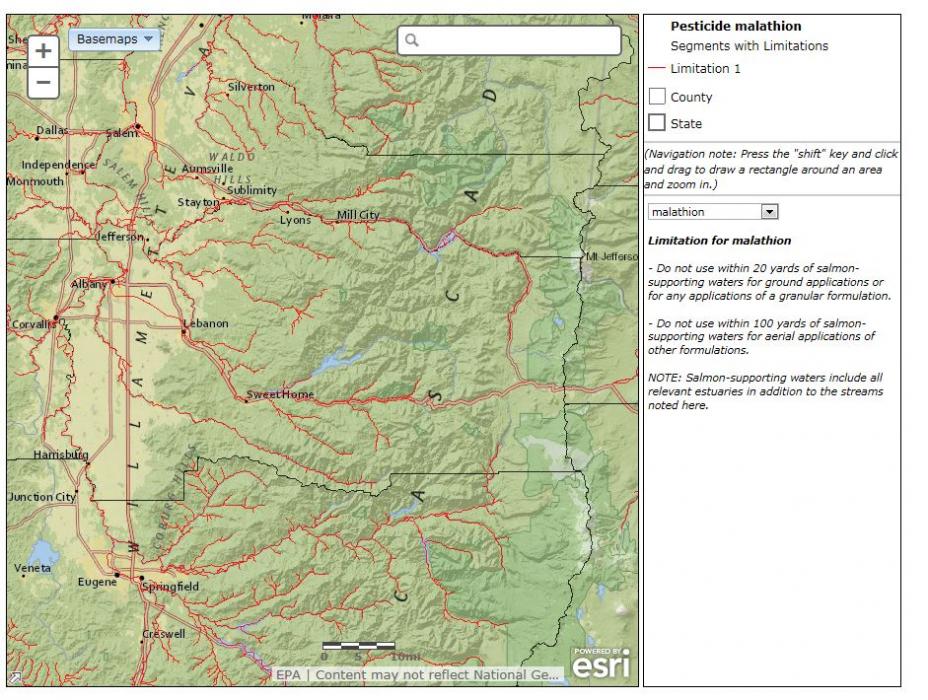
- Oceans
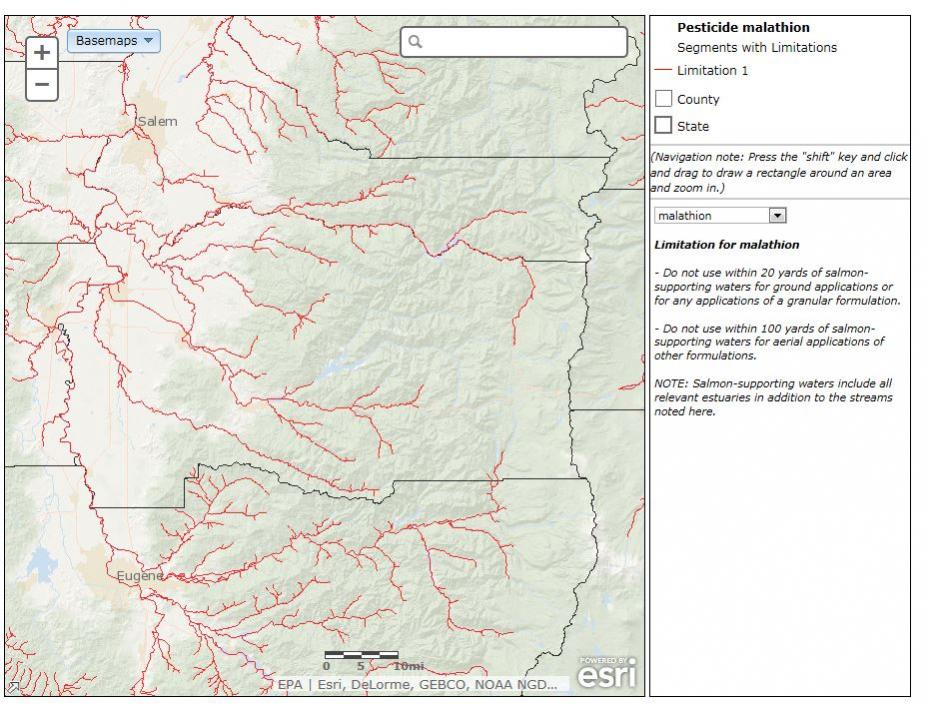
- OpenStreetMaps
- Zoom In and Out
Zoom Out
To zoom in, click on the “+” button in the upper-left corner. You can also zoom in by holding the shift button and using your mouse to draw a square around your location of interest. To zoom to a specific location enter the address, county name or landmark of interest in the “Location Search Box” in the top right corner.
Zoom Out
To zoom out, click on the “-” button in the upper-left corner.
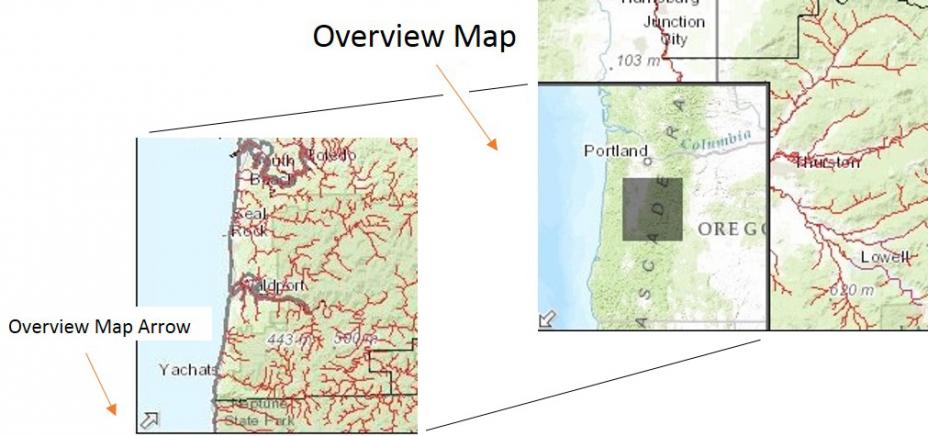
- Overview Map
Click on the arrow on the bottom-left corner to view an overview map within your window. To close this map click on the arrow a second time. The overview map option allows you to display a higher-level map that shows your window location.