National Compliance Initiative: Reducing Noncompliance with Drinking Water Standards at Community Water Systems
Problem
There are approximately 50,000 regulated drinking water systems that serve water to the same people year-round, referred to as Community Water Systems (CWSs). In FY 2018, 40 percent of the nation’s CWSs violated at least one drinking water standard. In addition, there were monitoring and reporting violations at more than 30 percent of CWSs, and health-based violations at 7 percent of CWSs.
Goal
This effort supports the FY 2018–FY 2022 Agency Strategic Plan, which calls for a 25 percent reduction by the end of FY 2022 in the number of CWSs that are out of compliance with health-based standards. An initial focus of this NCI is to work with the EPA’s Office of Water to increase capacity in states, tribes, and the EPA to address drinking water violations.
Results
During FY 2020, the initial year for implementation of this Initiative, the agency made significant progress on this NCI. The following are illustrative of the agency’s efforts in FY 2020 to improve drinking water qualtiy at community water systems (CWSs).
Expanded inspector capacity and technical expertise
- To support primacy agencies and maintain its direct implementation responsibilities, the Agency led or accompanied primacy programs during 54 onsite inspections and performed offsite compliance monitoring at 84 CWSs. The Agency also developed and provided web-based inspector training for EPA, state, and tribal inspectors. Working to rebuild EPA’s capacity, by the middle of calendar year 2020, EPA will have credentialed inspectors in every region.
Initiated a circuit rider program
- The Agency launched this program to provide effective on-the-ground assistance to help public water systems achieve and sustain environmental compliance. By the end of calendar year 2020, EPA will begin a circuit in every region.
Developed model to identify at-risk systems
- OECA piloted a predictive model to identify systems at risk of future serious violations to prompt early intervention.
Health Based Violations
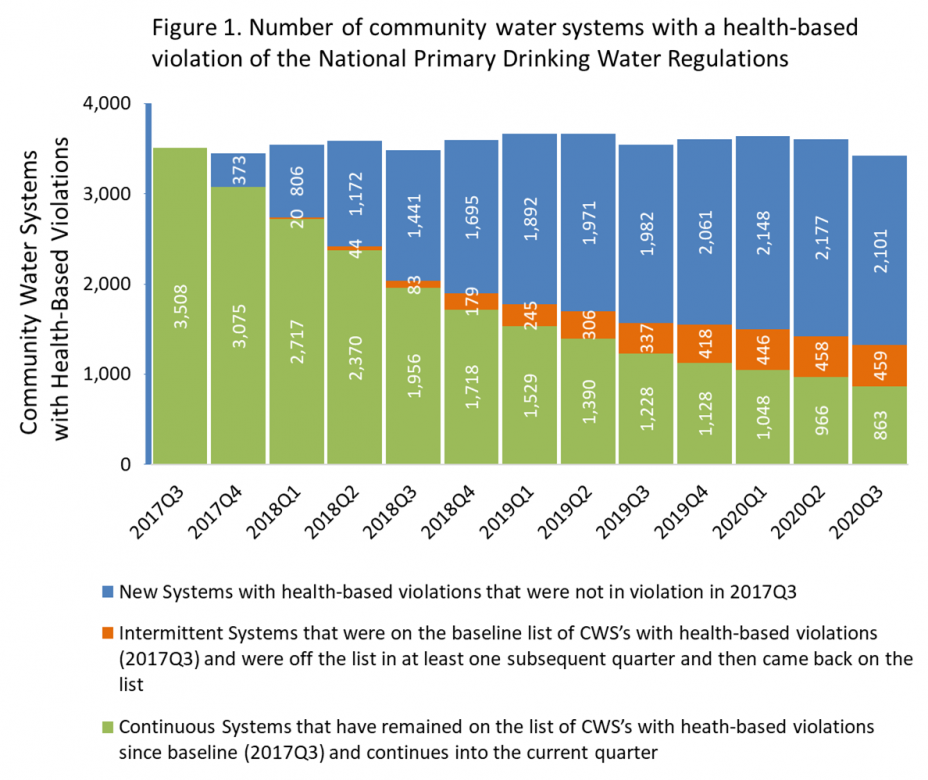
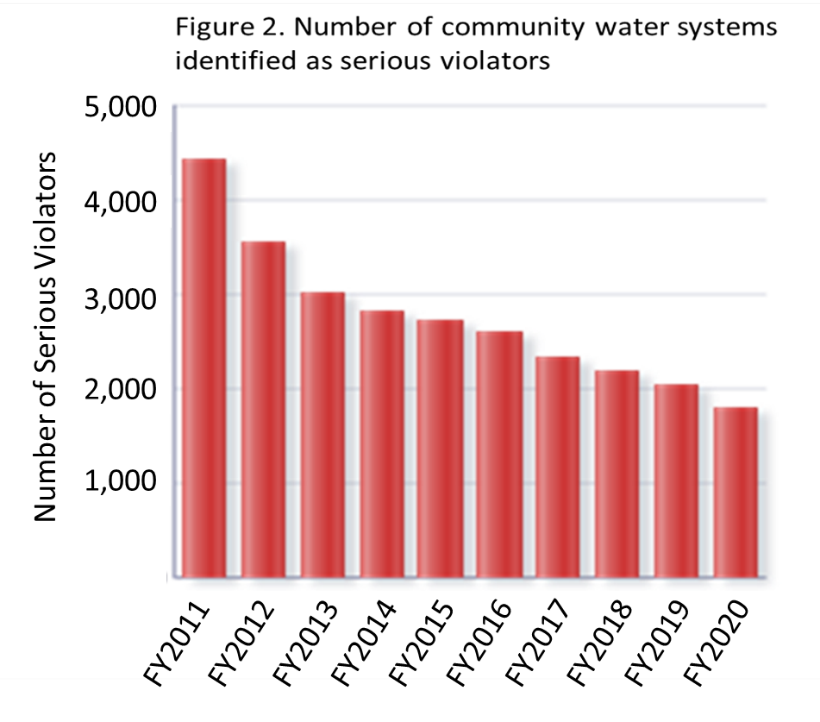
Cases
- Westchester Joint Water Works: Stage 2 Disinfectants and Disinfection Byproducts Rule violations. Westchester is a large CWS serving approximately 60,000 people in the Village of Mamaroneck and Village of Harrison in New York.
- City of Jackson, Mississippi: Emergency order issued to require repair and replacement of critical infrastructure.
- Wyoming: Multiple actions against systems in violations. EPA is the primacy agency in Wyoming.
- Tribal systems: Multiple actions against tribal systems. EPA is the primary enforcement agency in Indian country.
