Frequently Asked Questions for Disadvantaged Business Enterprises
Questions
- Where are the regulations that govern EPA’s DBE program?
- What are the DBE objectives?
- Who is covered by this rule?
- What MBE/WBE entities are included under EPA’s DBE program?
- Does EPA have a directory or link to certified MBEs/WBEs?
- What are the required Six Good Faith Efforts?
- What are some examples of documentation for the Six Good Faith Efforts?
- Who must report?
- What is the dollar threshold for the Simplified Acquisition Threshold?
- Does the MBE/WBE reporting procurement threshold apply to subrecipients, loan recipients and prime contractors? Should the recipient of an EPA direct assistance agreement only require reporting from its subrecipients, loan recipients and prime contractors if these entities’ procurement dollars exceed the $250K threshold?
- If I must report, when must the report be submitted?
- Where can I find the report?
- Which Simplified Acquisition Threshold amount is correct- the Simplified Acquisition Threshold amount listed on Form 5700-52A or the current Simplified Acquisition Threshold as set by the Office of Management and Budget?
- What should be reported?
- Where do I submit the report?
- What are the recordkeeping requirements?
- Are there special considerations for Tribes?
- Are there special considerations for EPA loan agreements?
- How do I find information on DOT’s and SBA’s certification programs?
Answers
Where are the regulations that govern EPA’s DBE program?
EPA’s DBE regulations are found at 40 CFR Part 33.
What are the DBE objectives?
The objectives of EPA’s DBE program are:
- to ensure nondiscrimination in the award of contracts under EPA financial assistance agreements;
- to operate harmoniously with the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision in Adarand Constructors, Inc. v. Pena, 515 U.S. 200 (1995);
- to help remove barriers to the participation of DBEs in the award of contracts under EPA financial assistance agreements; and
- to provide appropriate flexibility to recipients of EPA financial assistance in establishing and providing contracting opportunities for DBEs.
Who is covered by this rule?
All EPA assistance agreement recipients, any subrecipient of an EPA assistance agreement, and the first-tier prime contractor under an EPA assistance agreement must adhere to the requirements located in 40 CFR Part 33. Below is a visual diagram depicting what entities are covered by the EPA DBE program.
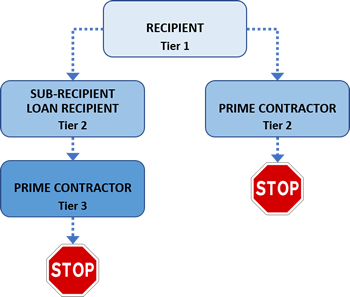
What MBE/WBE entities are included under EPA’s DBE program?
- Under EPA’s 8% statute, an entity must establish that it is owned or controlled by socially and economically disadvantaged individuals who are of good character and citizens of the United States. The statute presumes women to be socially and economically disadvantaged individuals.
- Under EPA’s 10% statute, an entity must establish that it is owned and controlled by socially and economically disadvantaged individuals who are of good character and citizens of the United States. The statute presumes Historically Black Colleges and Universities, Black Americans, Hispanic Americans, Native Americans, Asian Americans, Women and Disabled Americans are socially and economically disadvantaged individuals.
Note: Entities not covered by one of the two statutory presumptions for socially and economically disadvantaged individuals must meet the criteria listed in 40 CFR §33.202 and/or 40 CFR §33.203 to qualify for EPA’s DBE Program.
Does EPA have a directory or link to certified MBEs/WBEs?
No, EPA does not have a directory or list of certified MBEs/WBEs at this time. However, EPA recommends checking with the Small Business Administration, U.S. Department of Transportation, or the state in which your organization intends to do business. One possible resource that may be useful is: https://www.transportation.gov/DBE State Websites
What are the required Six Good Faith Efforts?
Recipients are required to make the following good faith efforts whenever procuring construction, equipment, services, and supplies under an EPA financial assistance agreement. A Native American recipient or prime contractor must follow the six good faith efforts only if doing so would not conflict with exiting Tribal or Federal law, including but not limited to the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act.
- Ensure DBEs are made aware of contracting opportunities to the fullest extent practicable through outreach and recruitment activities. For Indian Tribal, State, and Local Government recipients, this will include placing DBEs on solicitation lists and soliciting them whenever they are potential sources.
- Make information on forthcoming opportunities available to DBEs, arrange time frames for contracts, and establish delivery schedules, where the requirements permit, in a way that encourages and facilitates participation by DBEs in the competitive process. This includes, whenever possible, posting solicitations for bids or proposals for a minimum of 30 calendar days before the bid or proposal closing date.
- Consider in the contracting process whether firms competing for large contracts could subcontract with DBEs. For Indian Tribal, State, and Local Government recipients, this will include dividing total requirements when economically feasible into smaller tasks or quantities to permit maximum participation by DBEs in the competitive process.
- Encourage contracting with a consortium of DBEs when a contract is too large for one of these firms to handle individually.
- Use the services and assistance of the SBA and the Minority Business Development Agency of the Department of Commerce.
- If the prime contractor awards subcontracts, require the prime contractor to take the steps in items 1 through 5.
What are some examples of documentation for the Six Good Faith Efforts?
- Use of current bidders/solicitation list or databases that includes DBEs;
- Use of trade journals/databases (local or national);
- Date of last update to bidders/solicitation list or database;
- How were DBEs made aware of the solicitation;
- Where and when posted;
- Sample of letters or records of communication with DBEs, SBA, Minority Business Development Agency;
- Sample of advertisement/posting;
- How long/frequency of advertisement/posting;
- Document good faith efforts of contractors;
- Identify type of outreach that was conducted;
- Date of pre-bid conference;
- Attendance list for pre-bid conference;
- Participation date of last DBE procurement outreach conference;
- Process used to determine if large requirement could be divided into smaller requirements,
- Include unsuccessful bidders on database or list
Who must report?
Recipients must report if the combined total of funds budgeted for procuring supplies, equipment, construction or services exceeds the Simplified Acquisition Threshold.
What is the dollar threshold for the Simplified Acquisition Threshold?
As of June 20, 2018, the Simplified Acquisition Threshold is $250,000; however, the specific dollar amount changes over time for inflation. Recipients should use the current value that has been set by the Office of Management and Budget.
Does the MBE/WBE reporting procurement threshold apply to subrecipients, loan recipients and prime contractors? Should the recipient of an EPA direct assistance agreement only require reporting from its subrecipients, loan recipients and prime contractors if these entities’ procurement dollars exceed the $250K threshold?
The reporting threshold doesn’t apply to subrecipients and prime contractors as the requirement to report is only on the recipient.
If the recipient’s budget triggers the reporting requirement (i.e. the budgeted amounts for equipment, supplies, construction or contractual categories (which may be also included in “other”) is greater than the Simplified Acquisition Threshold (“SAT”) (currently $250,000)), then the recipient is required to complete and submit the MBE/WBE report form.
However, in order for the recipient to capture all dollars spent on MBEs and WBEs, the recipient will need to collect that information from their subrecipients and/or prime contractors.
If I must report, when must the report be submitted?
Recipients must submit annual reports by October 30th of each year. Final reports are due by October 30th or 90 days after the end of the project period, whichever comes first.
Where can I find the report?
Recipients are to use 5700-52A: MBE/WBE Utilization Under Federal Grants and Cooperative Agreements to report the required information.
Which Simplified Acquisition Threshold amount is correct- the Simplified Acquisition Threshold amount listed on Form 5700-52A or the current Simplified Acquisition Threshold as set by the Office of Management and Budget?
RAIN-2018-G04 (issued September 7, 2018) announced that the Simplified Acquisition Threshold has been increased by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) to $250,000. However, the form instructions have not been updated to reflect this revision. Despite the outdated information on the form, recipients are to use the current Simplified Acquisition Threshold of $250,000. If OMB should change this value again in the future, recipients should use whatever value OMB has set at that time.
What should be reported?
EPA requires that a recipient report the total amount of financial assistance expended on procurement and the amount awarded to a MBE or WBE on EPA Form 5700-52A.
Note: the amounts recorded on this form should only include actual expenditures and not unfulfilled commitments.
Where do I submit the report?
Please use the contact below which matches the awarding office which issued the EPA grant.
| Awarding Office | Contact Information |
|---|---|
| Headquarters | Via email to MBE.WBE@epa.gov. |
| Region 1 | Via email to the EPA Grants Specialist identified on the first page of the award agreement in the subject line. |
| Region 2 | Via email to Region2_GrantApplicationBox@epa.gov. |
| Region 3 | Via email to R3_MBE-WBE_Reports@epa.gov as a pdf file, or by postal mail to the attention of Diversity/EEO Manager (3DA10), U.S. EPA - Region III, 1650 Arch Street, Philadelphia, PA 19103-2029 with a courtesy copy to the EPA Grant Specialist identified on the first page of the award agreement in the subject line. |
| Region 4 | Via email to the EPA Grants Specialist identified on the first page of the award agreement in the subject line. |
| Region 5 | Via email to Region5Closeouts@epa.gov with the name of the Grants Specialist identified on the first page of the award agreement in the subject line. |
| Region 6 | Via email to R6_EPA_Grants_Programs@epa.gov with the name of the Grants Specialist identified on the first page of the award agreement in the subject line. |
| Region 7 | Via email to R7GRANTS@EPA.GOV. |
| Region 8 | Via email to the EPA Grants Specialist identified on the first page of the award agreement. |
| Region 9 | Via email to grantsregion9@epa.gov. |
| Region 10 | Via email to Andrea Bennett (Bennett.Andrea@epa.gov), Minority Business Enterprise/Woman Business Enterprise (MBE/WBE) Coordinator. |
What are the recordkeeping requirements?
A recipient must maintain all records documenting its compliance with the requirements of this program in accordance with applicable record retention requirements for the recipient's financial assistance agreement as required by 2 CFR Part 200 and any applicable terms and conditions.
Except as exempted by 40 CFR §33.501(c), a recipient of a Continuing Environmental Program Grant or other annual grant must create and maintain a bidders list. Such a list must only be kept until the grant project period has expired and the recipient is no longer receiving EPA funding under the grant. In addition, a recipient of an EPA financial assistance agreement to capitalize a revolving loan fund also must require entities receiving identified loans to create and maintain a bidders list if the recipient of the loan is subject to, or chooses to follow, competitive bidding requirements. For entities receiving identified loans, the bidders list must only be kept until the project period for the identified loan has ended. The following information must be obtained from all prime and subcontractors:
- Entity's name with point of contact;
- Entity's mailing address, telephone number, and e-mail address;
- The procurement on which the entity bid or quoted, and when; and
- Entity's status as an MBE/WBE or non-MBE/WBE.
Are there special considerations for Tribes?
(a) A Native American (either as an individual, organization, corporation, Tribe or Tribal Government) recipient or prime contractor must follow the six good faith efforts only if doing so would not conflict with existing Tribal or Federal law, including but not limited to the Indian Self-Determination and Education Assistance Act (25 U.S.C. 450e), which establishes, among other things, that any federal contract, subcontract, grant, or subgrant awarded to Indian organizations or for the benefit of Indians, shall require preference in the award of subcontracts and subgrants to Indian organizations and to Indian-owned economic enterprises.
(b) Tribal organizations awarded an EPA financial assistance agreement have the ability to solicit and recruit Indian organizations and Indian-owned economic enterprises and give them preference in the award process prior to undertaking the six good faith efforts. Tribal governments with promulgated tribal laws and regulations concerning the solicitation and recruitment of Native-owned and other minority business enterprises, including women-owned business enterprises, have the discretion to utilize these tribal laws and regulations in lieu of the six good faith efforts. If the effort to recruit Indian organizations and Indian-owned economic enterprises is not successful, then the recipient must follow the six good faith efforts. All tribal recipients still must retain records documenting compliance in accordance with §33.501 and must report to EPA on their accomplishments in accordance with §33.502.
(c) Any recipient, whether or not Native American, of an EPA financial assistance agreement for the benefit of Native Americans, is required to solicit and recruit Indian organizations and Indian-owned economic enterprises and give them preference in the award process prior to undertaking the six good faith efforts. If the efforts to solicit and recruit Indian organizations and Indian-owned economic enterprises is not successful, then the recipient must follow the six good faith efforts.
(d) Native Americans are defined in §33.103 to include American Indians, Eskimos, Aleuts and Native Hawaiians.
Are there special considerations for EPA loan agreements?
A recipient of an EPA financial assistance agreement to capitalize a revolving loan fund, such as a State under the Clean Water State Revolving Fund or Drinking Water State Revolving Fund or an eligible entity under the Brownfields Cleanup Revolving Loan Fund program, must require that borrowers receiving identified loans comply with the good faith efforts described in §33.301 and the contract administration requirements of §33.302. This provision does not require that such private and nonprofit borrowers expend identified loan funds in compliance with any other procurement procedures contained in 2 CFR part 200 Subpart D—Post Federal Award Requirements, Procurement Standards, or 40 CFR part 35 subpart O, as applicable.
