Small Business Resources
Small Businesses Engagement in the Green Power Market
Organizations, large and small, are exploring how to use green power to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help protect our planet. Smaller businesses’ and organizations’ growing commitments to use green power are an important force in supporting renewable energy resources. EPA is committed to supporting organizations interested in buying green power.
Below are some key considerations for smaller businesses and organizations when engaging in the green power market.
Does your local electricity supplier offer a green power product?
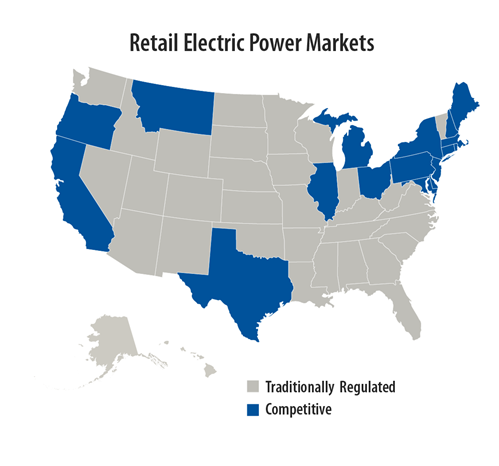
Depending on your state, you may have a choice in who generates your electricity (see states in blue on adjacent map). In states with competitive retail electric power markets, electricity suppliers compete for your business and you can shop to find electricity suppliers who offer green power product options. If your state is traditionally regulated (see states colored grey), check with your electricity supplier about green power product options.
In either case, utility green power products offer consumers renewable electricity, often at a small cost premium to standard electricity products, and consumers typically continue to be billed through a single billing arrangement.
Utility green power product offerings include Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs), which are purchased and retired on behalf of the customers who sign up for green power products and programs. RECs represent the technology and environmental attributes of electricity generated from renewable sources and are the currency used for credible green power purchases.
EPA recommends that consumers look for certified and verified green power products as a consumer best practice. Products that are certified and verified by an independent organization offer confidence that the product meets nationally-accepted standards for product quality and content and ensure the consumer is getting what they paid for. The Center for Resource Solutions’ Green-e program Exit is the only third-party certification program in the US. You can use their online tool to “Find Green-e Certified” Exit products and suppliers.
Does a retail renewable energy certificate (REC) product meet your needs?
Retail RECs are accessible to consumers nation-wide and offer a choice of renewable resources. Access to retail RECs are not limited by the state you live in, which allows organizations to purchase and use renewable electricity, support investments in renewable resource development, and protect the environment, even if green power products are not locally available from an electric supplier. When purchasing retail RECs, consumers will receive a separate bill from their electricity service.
By purchasing a REC, consumers gain exclusive rights to make claims about using or "being powered with" renewable electricity. Retail RECs are sold to consumers by retailers who buy in bulk from newer renewable resources, such as a wind farm. One-year purchases, but some retailers may have purchased the RECs from new renewable resources, such as a wind farm, in long-term contracts.
Certified and verified retail RECs are available and green power products certified by an independent third-party offer consumers a higher level of certainty about the integrity of their purchase and assurance that you will get what you have paid for. The Center for Resource Solutions’ Green-e program Exit is the only third-party certification program in the US. You can use their online tool to “Find Green-e Certified” Exit products and suppliers.
Engage in a shared renewables project
Engaging in shared renewables is an emerging procurement option allowing multiple customers (also sometimes referred to as project sponsors) to buy, lease, or subscribe to a portion of a renewable energy project that is typically in your county or state. This option is especially appealing to electricity customers who want to support new renewable resources but do not own their own home or have a home that is not suitable for an onsite renewable energy generator.
More than 15 states and the District of Columbia have authorized shared renewables or community solar for local utilities and their customers Exit IT, and there are active campaigns to enact shared renewables legislation in a number of other states. Some rural electric cooperatives Exit also offer programs or consumers the option to engage with shared solar projects.
Consumers should be aware that many subscriptions to shared renewables and community solar projects are not green power purchases because their purchase does not include RECs, which means the consumer or project sponsor is not receiving renewable electricity.
There are several advantages in engaging in a shared renewables project, such as allowing more consumers to support new renewable resources and reducing electric bills. By offering an on-bill credit for the power generated by the shared renewable project, many subscriptions promise to save you money.
Install an onsite solar project
Installing an onsite renewable energy project may be an option for some. There are generally two options:
- Self-Financing. Under this arrangement, the consumer pays for the onsite project. This approach requires an upfront investment, but the consumer can reduce reduced electric bills and can choose to be green powered by keeping the RECs generated by the onsite project.
- Third-Party Financing. Under this arrangement, the consumer enters into a contract or lease with a project developer who will own and operate the onsite renewable project on the consumer’s property. The consumer does not have to make an upfront investment, but they typically agree to purchase the electricity for 7-20 years. If the consumer wants green power, they must agree to also purchase RECs.
For onsite project development resources, visit EPA’s Toolbox for Renewable Energy Project Development. Consumers can get quotes from project developers using the EnergySage website Exit powered by DOE’s Sunshot program. When engaging with developers of solar projects, it is a consumer best practice to seek project developers that are certified designers and installers by North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP) Exit.
Relevant Resources
EPA’s Green Power Partnership program has a number of resources for smaller businesses and organizations interested in the green power market, including:
Guide to Purchasing Green Power
The Guide to Purchasing Green Power is an excellent place to start for organizations interested in buying green power. The guide provides information about the green power procurement process, different green power supply options, benefits of green power purchasing, as well as information on how to capture the greatest benefit from your purchase.
Appendix C provides an overview of the market and opportunities for the residential market and small businesses.
RECs and Claims Guidance
Organizations that choose green power generally want to make a claim (expressly or implied) about how they are making a difference with their purchase or installation. For information on making solar power use claims, see the Guide to Making Claims About Your Solar Power Use and for examples of acceptable claims see the Solar Power Use Claims webpage.
The Federal Trade Commission (PDF) (36 pp, 195K) Exit and National Association of Attorneys General green marketing guidance Exit have guides that apply to environmental claims regarding green power and renewable energy usage. The guides apply to any claim about the environmental attributes of products and services.
Past Webinars Relevant for Small Businesses
ENERGY STAR® Webinar: Renewable Energy Options for Small Businesses and Congregations
Electricity use is often the single largest source of an organization’s emissions and air pollution footprint, not to mention being a significant expense. Making the simple choice to use renewable energy can offer environmental, economic and community benefits. On this webinar, you will learn about the various options available in the market to buy green power through retail purchase, self-generation and direct purchase from a renewable project. You will learn about how to align your desired energy and environmental outcomes to specific green power supply options. You will learn about the role of renewable energy certificates and how they can support your organization meeting its renewable energy and carbon footprint reduction goals. Originally aired May 21, 2020. You may also listen to a recording of this session here Exit
