Utility Green Tariffs
What are Utility Green Tariffs?
Utility green tariffs are optional programs in regulated electricity markets offered by utilities and approved by state public utility commissions (PUCs) that allow larger commercial and industrial customers to buy bundled renewable electricity from a specific project through a special utility tariff rate.
This emerging green power utility offering in regulated markets provides larger energy customers an option to meet their varying sustainability and renewable energy goals, reduce long-term energy risks, and demonstrate commitment to the development of new renewable energy projects.
Utility green tariffs are an important innovation that increases consumers' ability to access green power. From 2012 to 2017, only 16 percent of corporate off-site purchase deals signed occurred between organizations and utilities in traditionally regulated markets, even though these areas produce approximately 40 percent of U.S. electricity.1 Utility green tariffs help bridge that gap, expanding the opportunity for organizations in traditionally-regulated states to buy bundled green power beyond utility green power products and unbundled RECs. As of October 2017, nearly a gigawatt of green power has been installed, is in development, or is under contract to be developed through utility green tariff programs.2
For more information about how to decide which potential green power procurement options are available for your organization, see the Green Power Screening tool.
How do Utility Green Tariff programs work?
Organizations in regulated electricity market can take advantage of a utility green tariff if it is available and they meet the program's eligibility requirements. The organizations that are eligible vary considerably between green tariff programs, so organization should check with their local utility to find out if they qualify.
Under a green tariff, utilities supply the organization with up to 100 percent renewable power from projects either owned by the utility or contracted with independent power producers in the local grid or utility region. Green tariff programs vary though in the exact mechanism which the utility uses to procure green power on behalf of the organization. Some programs allow customers to choose a "market-based rate"—ie. to peg their electric rate to the wholesale electricity market price.3 Other programs let the organization engage directly with the renewable generation project, encouraging competitive project selection and ensuring new renewable energy capacity is brought onto the grid. In other programs, the utility facilitates the organization's green power purchase through a type of power purchase agreement, called a "sleeved PPA," where the utility essentially passes a physical power purchase agreement (PPPA) that it has signed with a renewable energy project along to the consumer. In all green tariff programs, utilities avoid shifting program costs and risks to non-participating utility customers and only charge participating organizations for the cost of the renewable electricity.
Advantages and Challenges of Utility Green Tariffs
Advantages:
- Direct transaction/arrangement between an organization and local utility
- A new option for larger electricity customers in regulated markets to help meet their sustainability and renewable energy goals
- Price predictability and potential cost savings
- Enables organization to point to a specific, often local, renewable energy project as the source of its electricity
- Enables organization to procure renewable electricity from a project located in same grid region as their operations
Challenges:
- Only offered in a limited number of traditionally regulated states by a few utilities
- Generally only available to large electricity customers
- May require a long-term commitment
What is the difference between a Utility Green Tariff and a Utility Green Power Product?
Both options are offered by utilities to customers in traditionally-regulated markets, and in both options, the customer receives bundled green power (i.e. RECs alongside the underlying electricity). The two options are slightly different in their purchasing process, who they're available to, term of contract, and level of project specificity.
With a green tariff, eligible organizations buy bundled renewable energy from a specific project through their utility, usually through a longer-term agreement. With a green power product, customers, which can include residential customers, pay a cost premium as an extra line item on their electric bill to support an "off-the-shelf" renewable electricity product, which often is a mix of renewable energy resources. These are often shorter-term commitments and the renewable energy resource mix used to generate the green power can be intermittently changed by the utility.
How do I know if my state has Utility Green Tariffs?
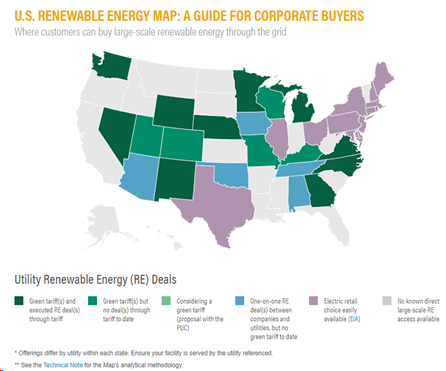
As of February 2018, 21 utility green tariffs in 15 states have been proposed or approved. The states are Colorado, Georgia, Kentucky, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Utah, Virginia, Washington, Wisconsin, and Wyoming.4 If you live in one of these states, your state has a traditionally regulated retail electricity market in which consumers have no choice but to purchase electricity from their local utility at prices regulated by the state and utility commission. Utility Green Tariffs are a relatively new option in regulated retail markets allowing qualifying organizations to procure bundled renewable electricity from specific renewable energy projects.
For a map showing the status of utility green tariff programs throughout the U.S., see the World Resource Institute's U.S. Green Tariffs Map (44 pp, 559K) Exit. Click on your state to see if your utility offers a green tariff program and if your organization meets the eligibility requirements.
What are some organizations that have used Utility Green Tariffs?
A number of larger IT firms are using green tariffs, including Apple and Google. These companies have taken advantage and helped create these options by negotiating for them with utilities, and in many cases, even advocated for and helped develop them. Apple purchases renewable energy through Nevada Energy's GreenEnergy Rider program, and Google utilizes North Carolina utility Duke Energy's green tariff.
Furthermore, a new type of "subscriber-style" green tariff, pioneered by Puget Sound Energy (PSE), has attracted organizational customers outside the tech industry. Green Power Partners REI, Starbucks, and Western Washington University are participating in PSE's Green Direct program. This program boasts some of the first retail, university, and city government green tariff participants.
Partner Case Study
Outdoor sports equipment retailer REI has been an EPA Green Power Partner since 2011, and won a Green Power Purchasing Leadership award in 2014. The company was a key partner encouraging Puget Sound Energy to develop the Green Direct program over the past decade.
Kirk Myers, REI's senior manager of sustainability, said, "REI has long advocated for innovative and impactful renewable energy programs that make business sense. We began conversations with PSE several years ago about how we can increase access to renewable energy, not just for REI but for companies throughout the Puget Sound region. It's great to see our long collaboration with PSE come to life with this tariff and serve several local companies, cities and government entities." REI will power its headquarters and five local Washington stores through the PSE green tariff program. The company already operates 100% on renewable energy and has kept its energy use nearly flat while doubling sales since 2008.5 REI's work to promote green tariffs is a great example of corporate leadership increasing the available green power purchasing options and advancing the U.S. voluntary market for green power.
Additional Resources:
- Green Tariffs Take Off in the US, Expand Access to Renewable Energy Exit. World Resources Institute Blog, October 26, 2016
- Emerging Green Tariffs in U.S. Regulated Electricity Markets Exit. World Resources Institute. Accessed June 25, 2018
- Utility Green Tariff Programs: Considerations for Federal Agencies (PDF) (24 pp, 658K) Exit. National Renewable Energy Laboratory, May 4, 2017
- https://facilityexecutive.com/2017/10/buying-renewable-energy-no-matter-where/ Exit
- Ibid
- Ibid
- http://wriorg.s3.amazonaws.com/s3fs-public/emerging-green-tariffs-in-us-regulated-electricity-markets_0.pdf (PDF) (44 pp, 559K) Exit
- https://www.greentechmedia.com/articles/read/washington-state-spearheads-a-novel-clean-energy-solution-for-starbucks-re#gs.Nu5enCo Exit