Radiation Resources Outside of EPA
There are two forms of radiation: non-ionizing and ionizing. Non-ionizing radiation has enough energy to move atoms around in a molecule or cause them to vibrate. Power lines, cell phones and smart meters are some sources of non-ionizing radiation.
Ionizing radiation is sufficiently energetic that it can knock electrons out of atoms. Ionizing radiation can break DNA strands and cause mutations that can lead to cancer. Radioactive elements, cosmic radiation from space, and medical x-ray machines are some sources of ionizing radiation. (See Types of Ionizing Radiation.)
EPA sets protective limits on ionizing radiation in the environment resulting from human use of radioactive elements such as uranium. (See EPA’s Role in Radiation Protection.) Information about common sources of radiation regulated by other agencies is below.
On this page:
- Radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum
- Power lines
- Electronic devices
- Cell phones
- Smart meters
- Medical use of radiation
- Nuclear power plants
- Imported goods
Radiation in the Electromagnetic Spectrum
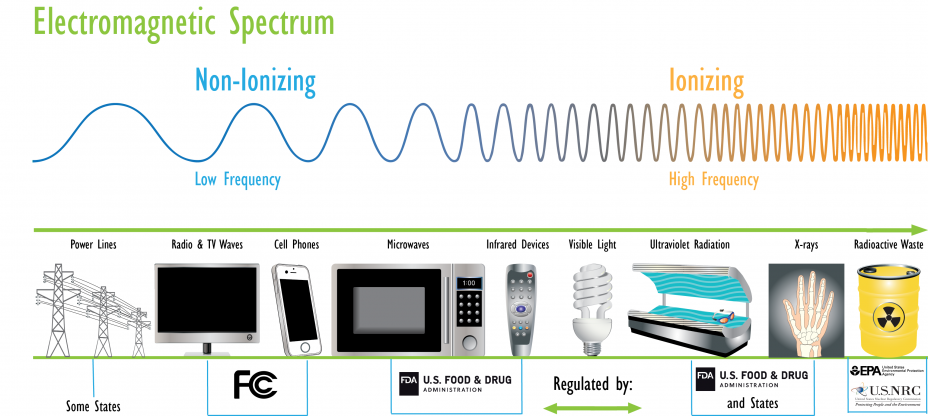 Example sources of non-ionizing radiation and the agencies that regulate them are on the left.
Example sources of non-ionizing radiation and the agencies that regulate them are on the left.
Example sources of ionizing radiation and the agencies that regulate them are on the right.
Power Lines
Power lines emit electric and magnetic fields (EMF), which are forms of non-ionizing radiation. There are no U.S. federal standards limiting residential or occupational exposure to EMF from power lines. For more information, see pages from the following organizations:
- World Health Organization - Electromagnetic FieldsExit
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences - EMF: Electric and Magnetic Fields Associated with the Use of Electric Power
Electronic Devices
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) sets standards for electronic devices that emit non-ionizing or ionizing radiation. For more information, see FDA’s page:
Cell Phones
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) sets limits on exposure to the electromagnetic radiation from cell phones and towers. For more information, see FCC’s pages:
- Wireless Devices and Health Concerns
- Radio Frequency Safety
- Questions and Answers about Biological Effects and Potential Hazards of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields
- Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) for Cellular Telephones
Smart Meters
Smart meters are equipped with a cellular transmitter that works using electromagnetic radiation. The FCC sets exposure limits for the electromagnetic radiation emitted by smart meters. For more information, see FCC’s page:
Medical Use of Radiation
Some medical procedures use ionizing radiation to help diagnose or treat illnesses. These procedures can include x-rays, CT scans, and radiation therapy to treat cancer.
- FDA regulates medical devices and ensures device safety in all medical settings. For more information, see FDA’s page:
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides information about medical procedures that use radiation. For more information, see CDC’s page:
- The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) regulates the manufacture and use of radioactive materials in nuclear medicine, radiation therapy and research. For more information, see NRC’s pages:
- EPA has an indirect role in the use of radiation in medicine. EPA develops and issues general radiation guidance to other federal agencies as a reference to develop rules and regulations to protect public health. For more information, see our page:
Nuclear Power Plants
- The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) licenses and regulates nuclear power plants. For more information, see NRC’s pages:
- The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) oversees radiological emergency response planning for state and local authorities in the event of a nuclear power plant incident. For more information, see:
- EPA plays a limited role in regulating nuclear power. EPA sets limits on radiation exposure to the public from normal operations of uranium fuel facilities. For more information, see our page:
Imported Goods
The U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) screens imported products for harmful substances. For more information, see CBP’s page:
