Overview of Air Pollution from Transportation
- What vehicles, engines and pollutants are regulated by EPA?
- Health and environmental impacts of air pollution
- Health and environmental impacts of climate change
What Vehicles, Engines and Pollutants are Regulated by EPA?
EPA emissions standards for vehicles and engines cover everything from weed whackers to locomotives.
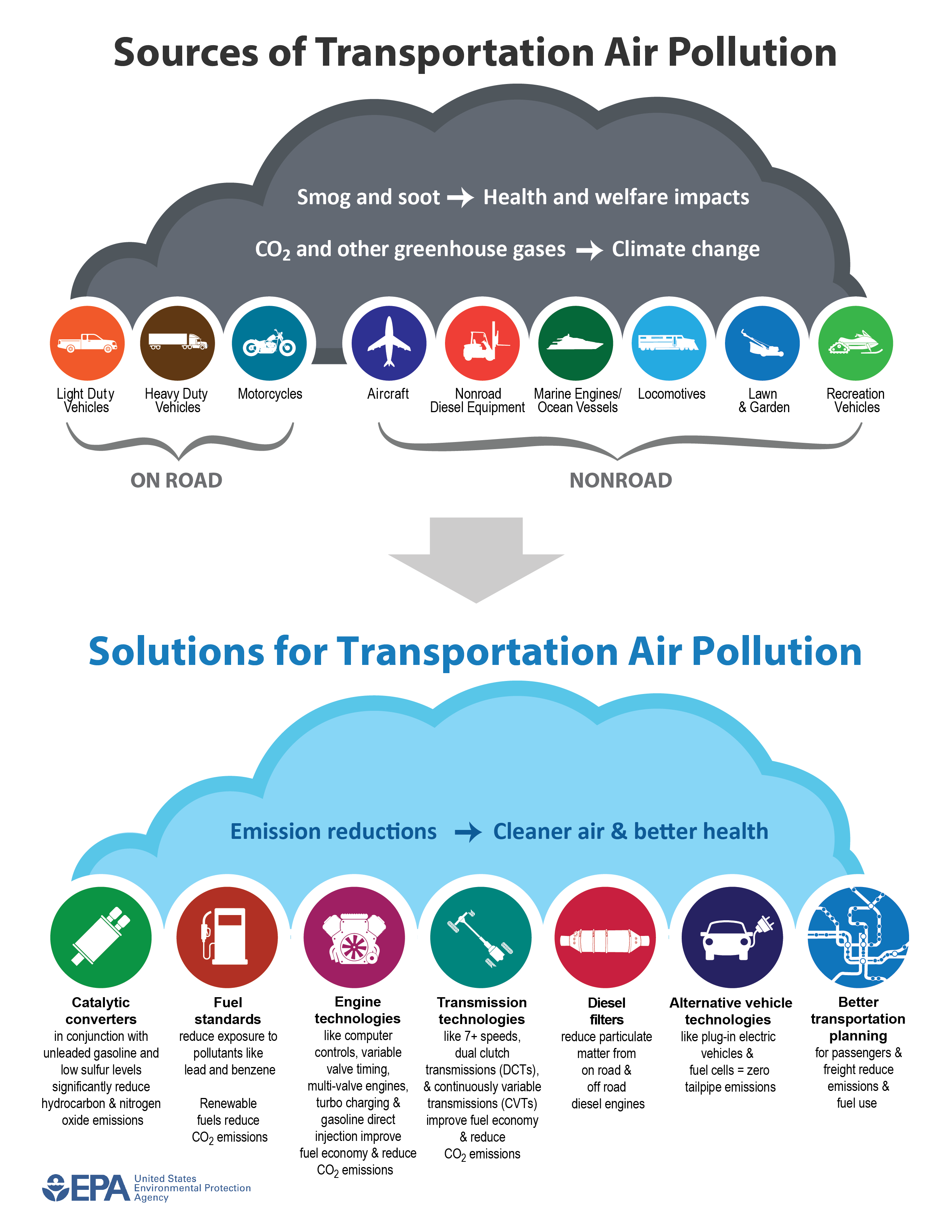
Text version of infographic
Health and Environmental Impacts of Air Pollution
Mobile sources of air pollution emit ozone, particle pollution, and air toxics. The health effects of mobile source air pollution affect millions of people, especially people who live near busy roads. The environmental impacts include haze in many parts of the U.S., including many of our national parks and wilderness areas, and the acidification of lakes and streams.
Health and Environmental Impacts of Climate Change
The impacts of climate change include warming temperatures, changes in precipitation, increases in the frequency or intensity of some extreme weather events, and rising sea levels. These impacts threaten our health by affecting the food we eat, the water we drink, the air we breathe, and the weather we experience.
