Quantile Regression: Chironomid richness vs. Metal Toxicity Units
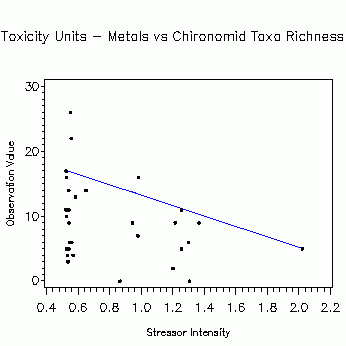
Plot
- Analysis: Quantile regression
- Independent variable: Metal Toxicity Units
- Dependent variable: Chironomid taxa richness
- Key: dot=observation; line= 90th quantile
- Sample size: n = 37
Model
- Chironomid taxa richness = 21.221 - 8.018*(Metal Toxicity Units)
- Date: 12 November, 2006
| Variable | Estimate | Lower CL | Upper CL | Test Type | Statistic | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | 21.221 | -1.282 | 43.723 | T value | 1.914 | |
| Metal Toxicity Units | -8.018 | -40.937 | 24.902 | T value | -0.494 | 0.624 |
| WALD | Chi2 | 0.244 | 0.621 | |||
| Likelihood Ratio | Chi2 | 1.408 | 0.235 |
Data Analysis
- Model generated using SAS Proc QUANTREG with the smoothing algorithm. The WALD and Likelihood test statistics were used to test the linear null hypothesis, H0: slope=0.
- Analysis for sites classified as pH neutral, but with strong AMD input.
- Metal Toxicity Units (TU) were calculated as sum of the ratios of each measured metal concentration with the criterion for that metal.
- Replicate visits to a site were not excluded from the data set.
Data Origin
- Agency: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
- Program: Environmental Monitoring and Assessment Program (EMAP)
- Project: Colorado Metals Belt Stream Assessment (EPA Region 8)
- Filenames: Files benmet, fishmet and chem downloaded from the Surface Waters Information Management (S.W.I.M.S.) database web site
Sampling Design
- Data collected 1994 through 1995.
- Analyzed metals and metalloids: aluminum, arsenic, cadmium, chromium, copper, iron, manganese, nickel, lead, selenium, silver, zinc.
- A description of the sampling methods may be found in the EMAP West Methods Manual for Streams found on the S.W.I.M.S. database web site.
