The Decoupled Direct Method in Three Dimensions (CMAQ-DDM-3D)
The Decoupled Direct Method in Three Dimensions (DDM-3D) provides CMAQ concentration and deposition sensitivity information for user specified model parameters.
In air quality modeling, sensitivities measure the response of a model output to a change in one or several predefined model parameters. In policy applications, the parameters of interest are usually emissions and the output of interest is pollutant concentrations. We may be interested in emissions from a particular geographical region, like an urban area, a group of states, or a country, and/or emissions from a particular source, such as wildfires, electricity generating units (EGUs), or light duty diesel trucks.
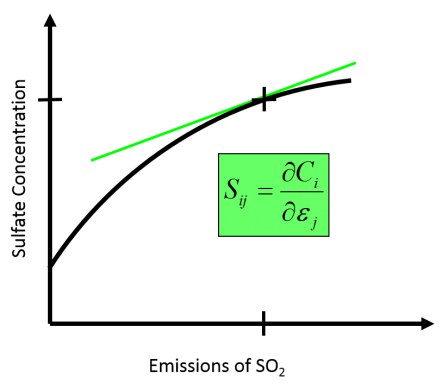 A hypothetical relationship between emissions of SO2 and sulfate concentrations. The green tangent line illustrates the sensitivity of sulfate concentration to emissions of SO2.Emissions sensitivities can be calculated by simply running the air quality model twice – once with standard emissions inputs, and once with the emissions of interest adjusted in some way. The difference in outputs between the two runs in relation to the size of the adjustment then becomes the model sensitivity. While this process is fairly easy to implement and interpret, it quickly becomes computationally complex as the number of desired sensitivities increases. For example, calculating sensitivity to EGU emissions from 10 southeastern states in the U.S. would require 11 separate air quality model simulations.
A hypothetical relationship between emissions of SO2 and sulfate concentrations. The green tangent line illustrates the sensitivity of sulfate concentration to emissions of SO2.Emissions sensitivities can be calculated by simply running the air quality model twice – once with standard emissions inputs, and once with the emissions of interest adjusted in some way. The difference in outputs between the two runs in relation to the size of the adjustment then becomes the model sensitivity. While this process is fairly easy to implement and interpret, it quickly becomes computationally complex as the number of desired sensitivities increases. For example, calculating sensitivity to EGU emissions from 10 southeastern states in the U.S. would require 11 separate air quality model simulations.
An alternative approach to calculate sensitivities is available with the CMAQ model – CMAQ-DDM-3D. CMAQ-DDM-3D is a separately downloadable version of the CMAQ model that allows for sensitivity calculation simultaneously with the standard concentrations and deposition fields. This is done by altering the existing model algorithms to allow for sensitivity propagation through every science module in CMAQ. While CMAQ-DDM-3D does require more computational resources than standard CMAQ, it scales much more favorably with the number of desired calculations.
Besides emissions, sensitivities to other model parameters can also be calculated. Currently, CMAQ-DDM-3D can be used for sensitivity to emission rates, boundary conditions, initial conditions, reaction rates, potential vorticity, or any combination of these parameters. Second order sensitivity calculations, or sensitivity of sensitivity, are also available.
- CMAQ-DDM-3D is downloadable with the standard release of the model.
- For documentation please refer to the CMAQ-DDM-3D User's Guide. Exit
References
Cohan, D.S., & Napelenok, S.L. (2011). Air Quality Response Modeling for Decision Support. Atmosphere, 2(3), 407-425. doi: 10.3390/atmos2030407Exit
Napelenok, S.L., Cohan, D.S., Odman, M.T., & Tonse, S. (2008). Extension and evaluation of sensitivity analysis capabilities in a photochemical model. Environmental Modelling & Software, 23(8), 994-999. doi: 10.1016/j.envsoft.2007.11.004Exit
Napelenok, S.L., Cohan, D.S., Hu, Y.T., & Russell, A.G. (2006). Decoupled direct 3D sensitivity analysis for particulate matter (DDM-3D/PM). Atmospheric Environment, 40(32), 6112-6121. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2006.05.039Exit
