LakeCat Dataset - ReadMe
Updates & Corrections (Latest update - November 5, 2018)
Be sure to check here for recent updates and corrections to the LakeCat Dataset.
On this page:
- LakeCat Citation
- Geospatial Framework and Terms
- Data Structure & Distribution
- Linking the NHDPlusV2 and LakeCat
- Using LakeCat with ESRI ArcMap
LakeCat Citation
- A detailed description of the LakeCat Dataset and its development is now available in the journal Freshwater Science.
- Please include the following citation in any publication or presentation including LakeCat data: Hill, Ryan A., Marc H. Weber, Rick Debbout, Scott G. Leibowitz, Anthony R. Olsen. 2018. The Lake-Catchment (LakeCat) Dataset: characterizing landscape features for lake basins within the conterminous USA. Freshwater Science doi:10.1086/697966.
Geospatial Framework and Terms
The LakeCat Dataset was built using these components of the NHDPlusV2 geospatial framework:
- Lake - NHD waterbody (NHDWaterbody.shp) with FTYPE of ‘LakePond’ or ‘Reservoir’ (dark blue and light blue polygons in Fig. 1).
- On-network lakes - Lakes that intersected with the NHD stream network. In Fig. 1, the dark blue polygon intersects with the stream network and is an on-network lake.
- Off-network lakes - Lakes that were geographically isolated from the NHDPlusV2 stream network. The light-blue polygon in Fig. 1 is an off-network lake.
- COMID - A unique ID used by NHDPlusV2 found within NHDWaterbody.shp.
- UID - Unique identifier used in the custom geospatial framework developed for LakeCat. These IDs are created when rasters of off-network lake are made and are used during catchment delineation and when landscape metrics are summarized. These IDs are an intermediate step to produce summaries that are reported for lake COMIDs. Held in off-network.shp file attribute table for referencing.
- Catchment (Cat) - Portion of landscape that drains directly to a lake, excluding any contributions from upslope (off-network) or upstream (on-network) lakes or associated catchments. In LakeCat, the term catchment always refers to a local area of landscape that drains to a lake, but how this area is determined depends whether the lake is on or off of the NHDPlusV2 stream network.
- On-network catchment- On-network lake catchments are produced and distributed as part of the NHDPlusV2 stream network and catchment files. These catchments have the same definition as catchments within the NHDPlusV2 and StreamCat. The orange outlines in Fig. 1 are catchment boundaries for NHDPlusV2 stream segments. The three catchments that intersect with the on-network lake comprise the local catchment for this lake. For on-network lakes, watershed summaries are drawn diretly from StreamCat for the local-subcatchment that is the furthest downstream (see Fig. 1).
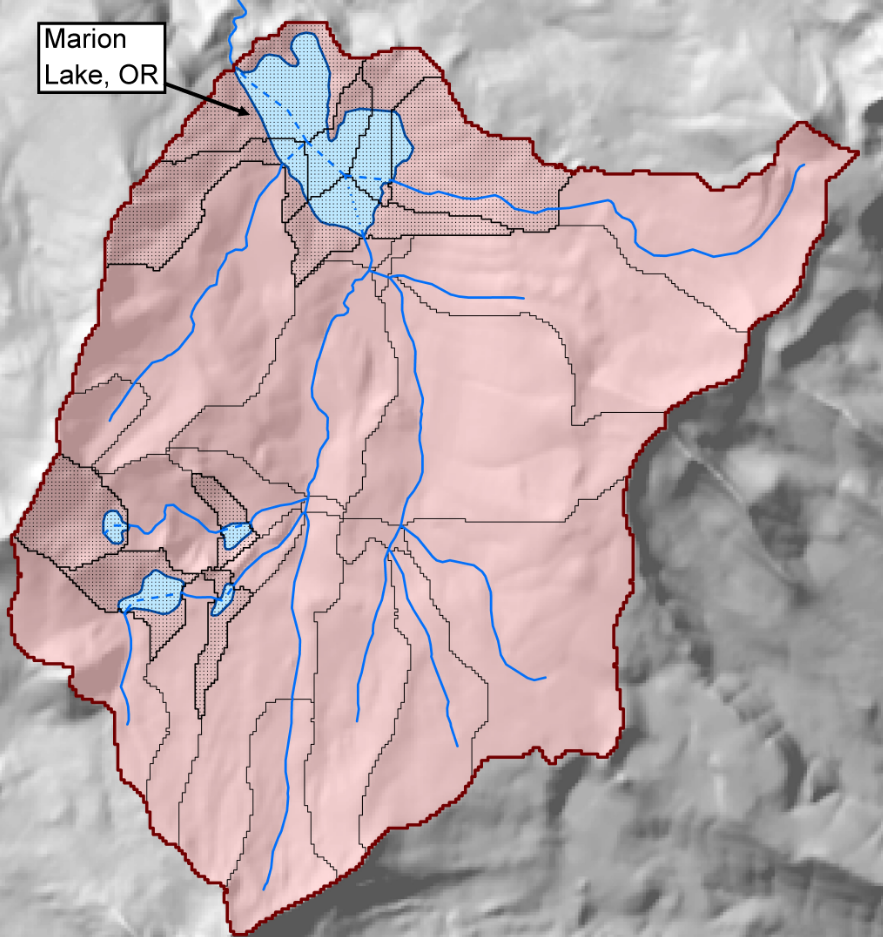 Figure 1. Example of on-network lakes and their associated catchments. On-network lakes intersect with NHDPlusV2 stream lines and often have several tributaries with separate catchments (black stippled catchments of Lake Marion). LakeCat aggregates the local catchments that intersect with each lake polygon and reports catchemnt-level statistics for these combined catchments. The set of hydrologically-linked catchments that feed to Lake Marion, OR are in pink. Figure from Hill et al. (2018).
Figure 1. Example of on-network lakes and their associated catchments. On-network lakes intersect with NHDPlusV2 stream lines and often have several tributaries with separate catchments (black stippled catchments of Lake Marion). LakeCat aggregates the local catchments that intersect with each lake polygon and reports catchemnt-level statistics for these combined catchments. The set of hydrologically-linked catchments that feed to Lake Marion, OR are in pink. Figure from Hill et al. (2018).
- Off-network catchment- Off-network catchments are produced by the USEPA with the ESRI Watershed tool. These catchments delineate an area that is only a portion of an NHDPlusV2 catchment (e.g., yellow stippled polygon in Fig. 2).
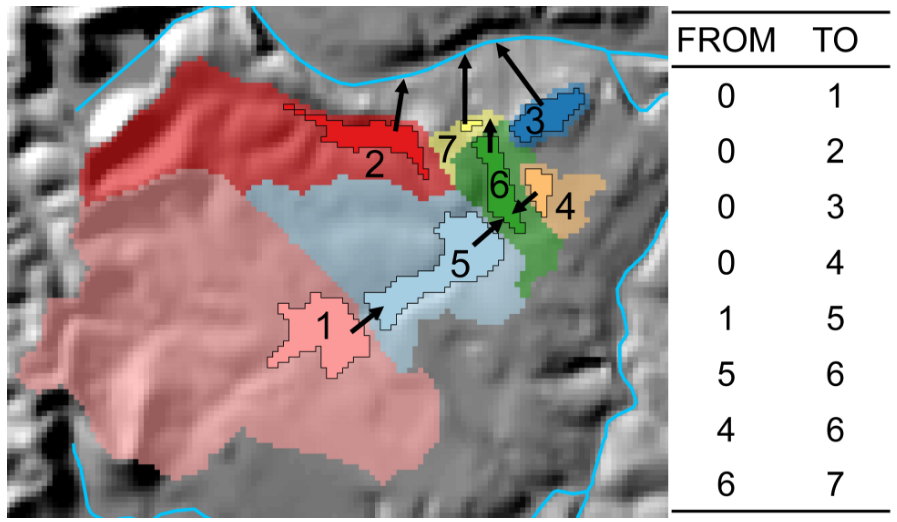 Figure 2. Example of off-network lakes (opaque with black outline) and their local catchments (semi-transparent). Numbers within lakes are unique identifiers and arrows indicate the direction of hydrologic connection among lake catchments. Hydrologic connections among lake catchments can be represented with a toplogy table. Figure from Hill et al. (2018).
Figure 2. Example of off-network lakes (opaque with black outline) and their local catchments (semi-transparent). Numbers within lakes are unique identifiers and arrows indicate the direction of hydrologic connection among lake catchments. Hydrologic connections among lake catchments can be represented with a toplogy table. Figure from Hill et al. (2018).
- Watershed (Ws) - Set of hydrologically-connected catchments, including all nested upstream (on-network) or upslope (off-network) lake catchments.
Data Structure & Distribution
Data are distributed by major data source (e.g., STATSGO Soils, National Land Cover Database).
Each table contains ancillary information about data completeness followed by catchment and watershed metrics:
- COMID - Lake unique identifier that can be linked to lakes within the NHDPlusV2 NHDWaterbody.shp shapefile.
- CatAreaSqkm - Area of catchment (km2).
- CatPctFull - % of lake catchment that overlaps with landscape layer. Accounts for areas of NoData pixels and international borders.
- WsAreaSqkm - Area of watershed (km2).
- WsPctFull - % of lake watershed that overlaps with landscape layer. Accounts for areas of NoData pixels and international borders.
- inStreamCat - Flag identifying lakes that intersected with NHDPlusV2 stream lines (value = 1) and lakes that did not intersect stream lines (value = 0). Rows with value = 1 have catchment and watershed metrics that were drawn directly from the StreamCat Dataset.
- Cat Metrics - Suite of catchment-level metrics with ‘Cat’ suffix in name.
- Ws Metrics - Suite of full watershed-level metrics with ’Ws" suffix in name.
Linking the NHDPlusV2 and LakeCat
- The LakeCat Dataset was built using NHDPlusV2 lakes and shares a common identifier with the NHDPlusV2. This unique identifier is COMID in both the NHDPlusV2 waterbody shapefiles (NHDWaterbody.shp) and LakeCat Dataset.
- Users can join LakeCat data tables to lake shapefiles (NHDWaterbody.shp) that are available for download by HydroRegion or as part of the national seamless geodatabase.
- It is strongly recommended that potential users of the LakeCat Dataset first familiarize themselves with the NHDPlusV2 (see NHDPlusV2 User Guide).
Using LakeCat with ESRI ArcMap
- LakeCat tables are distributed as zipped comma-delimited text files that must be uncompressed before importing to ArcMap. The data types of some fields can be misinterpreted when imported to ArcMap (e.g., text rather than number or long rather than double). This misinterpretation can cause problems when joining StreamCat tables to ESRI shapefiles.
- To work properly within the ArcMap environment, it is recommended that users download and store the initialization (‘schema.ini’) file in the same directory that contains any downloaded LakeCat files. The schema.ini file will ensure that ArcMap correctly interprets LakeCat column types.
