Particulate Matter (PM) Basics
- What is PM, and how does it get into the air?
- What are the harmful effects of PM?
- What is being done to reduce particle pollution?
What is PM, and how does it get into the air?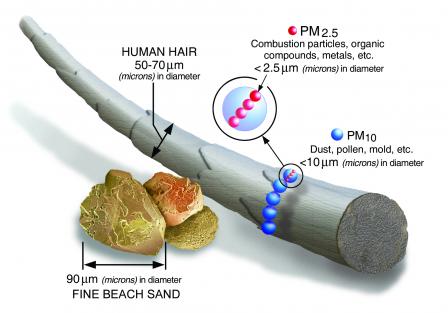 Size comparisons for PM particles
Size comparisons for PM particles
PM stands for particulate matter (also called particle pollution): the term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. Some particles, such as dust, dirt, soot, or smoke, are large or dark enough to be seen with the naked eye. Others are so small they can only be detected using an electron microscope.
Particle pollution includes:
- PM10 : inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 10 micrometers and smaller; and
- PM2.5 : fine inhalable particles, with diameters that are generally 2.5 micrometers and smaller.
- How small is 2.5 micrometers? Think about a single hair from your head. The average human hair is about 70 micrometers in diameter – making it 30 times larger than the largest fine particle.
Sources of PM
These particles come in many sizes and shapes and can be made up of hundreds of different chemicals.
Some are emitted directly from a source, such as construction sites, unpaved roads, fields, smokestacks or fires.
Most particles form in the atmosphere as a result of complex reactions of chemicals such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides, which are pollutants emitted from power plants, industries and automobiles.
What are the Harmful Effects of PM?
Particulate matter contains microscopic solids or liquid droplets that are so small that they can be inhaled and cause serious health problems. Some particles less than 10 micrometers in diameter can get deep into your lungs and some may even get into your bloodstream. Of these, particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter, also known as fine particles or PM2.5, pose the greatest risk to health.
Fine particles are also the main cause of reduced visibility (haze) in parts of the United States, including many of our treasured national parks and wilderness areas.
Learn more about health and environmental effects
What is Being Done to Reduce Particle Pollution?
EPA regulates inhalable particles. Particles of sand and large dust, which are larger than 10 micrometers, are not regulated by EPA.
EPA’s national and regional rules to reduce emissions of pollutants that form PM will help state and local governments meet the Agency’s national air quality standards. Learn about how air quality standards help reduce PM.
How Can I Reduce My Exposure to PM?
You can use air quality alerts to protect yourself and others when PM reaches harmful levels:
AirNow: Every day the Air Quality Index (AQI) tells you how clean or polluted your outdoor air is, along with associated health effects that may be of concern. The AQI translates air quality data into numbers and colors that help people understand when to take action to protect their health.
- Go to About AirNow to learn how you can get AQI notifications.
- Also learn how the Air Quality Flag Program can help air agencies, schools, and other community organizations to notify their citizens of harmful conditions and adjust outdoor physical activities as needed.
