Environmental Professional’s Guide to Lean and Six Sigma: Appendix D
Environmental Glossary
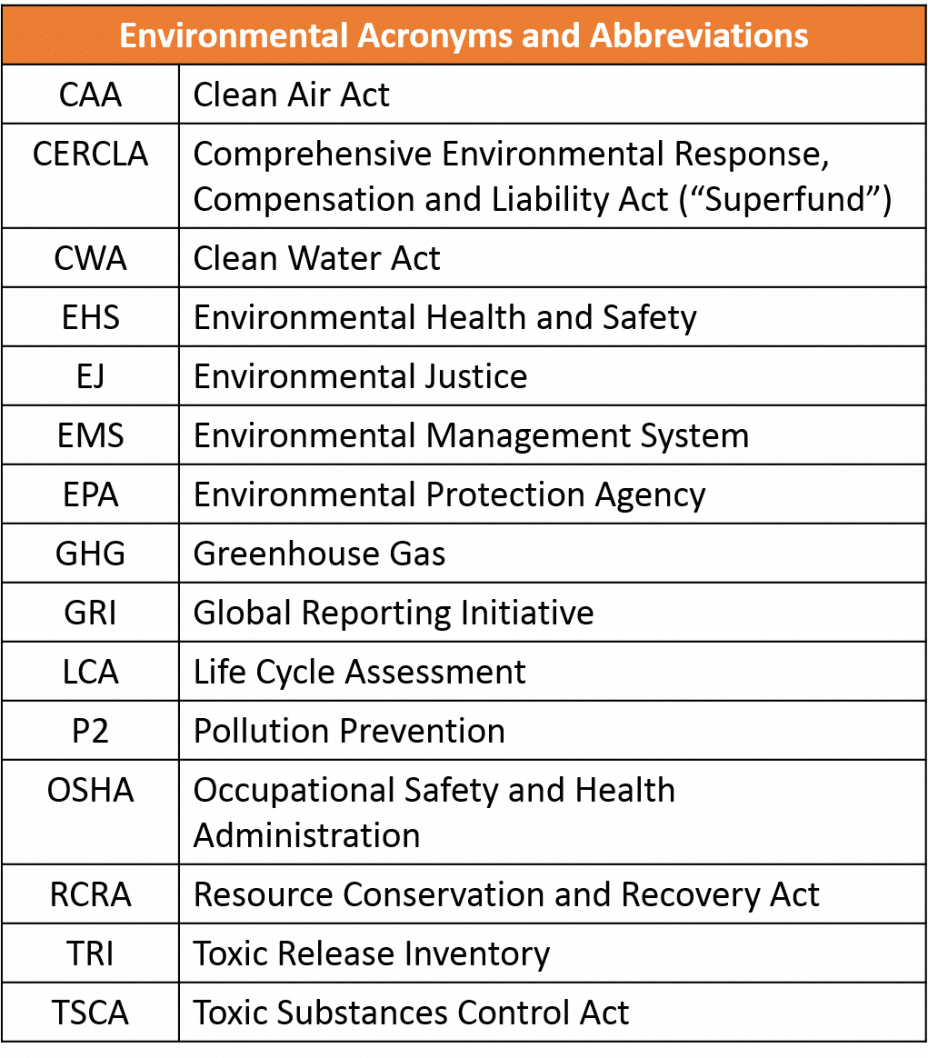
- Environmental Acronym and Abbreviation List
- Lean and Environment Terms and Definitions
- Toolkit Navigation
Environmental Terms and Definitions
| B | C | E | G | L | N | O | S | T | W |
|---|
B
Biofuel - Fuel created from renewable, biological sources such as plants or animal byproducts, but excluding biological material (such as natural gas, coal, or methane) that has been transformed by geological processes.
C
Carbon Footprint - The total amount of greenhouse gases emitted directly or indirectly through any human activity, typically expressed in equivalent tons of carbon dioxide.
Clean Air Act (CAA) - Federal legislation passed in 1970 and amended in 1990 that authorizes the EPA to set National Ambient Air Quality Standards and to regulate industry in order to meet those maximum emissions levels.
Clean Water Act (CWA) - Federal legislation passed in 1972 and amended in 1976 that requires the EPA to set maximum pollutant levels for each known contaminant in U.S. surface waters and authorizes the EPA to regulate industrial discharge in order to meet those standards.
Closed-loop Recycling - A process of utilizing a recycled product in the manufacturing of a similar product or the remanufacturing of the same product.
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (CERCLA) - Federal legislation passed in 1980 that established a tax on the petroleum and chemical industries to fund cleanup of hazardous waste sites, as well as establishing EPA authority to assign responsibility for that cleanup to the polluters or purchasers of contaminated land. Often referred to as “Superfund.”
Corporate Social Responsibility - The continuing commitment by businesses to behave ethically and contribute to economic development while improving the quality of life of the workplace as well as the local community and society at large.
E
Ecological Footprint - The total amount of land, food, water, and other resources used by, or the total ecological impact of, a person or organization’s subsistence; usually measured in acres or hectares of productive land.
Environmental Justice - The concept of equal access to environmental resources and protection from environmental hazards regardless of race, ethnicity, national origin, or income.
G
Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) - A reporting standard generally accepted to be the leading international standard for reporting social, environmental, and economic performance.
Green Building - A comprehensive process of design and construction that employs techniques to minimize adverse environmental impacts and reduce the energy consumption of a building, while contributing to the health and productivity of its occupants.
Green Design - The design of products, services, buildings, or experiences that are sensitive to environmental issues and achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness in terms of energy and materials use.
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) - A gas that contributes to the natural greenhouse effect, whereby heat is trapped within the Earth’s atmosphere, including: carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons and sulfur hexafluoride.
L
LEED Certification - An acronym for Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design, a program sponsored by the United States Green Building Council that creates standards for developing high performance, sustainable buildings.
Life Cycle Analysis (LCA) - A process of evaluating the effects of a product or its designated function on the environment over the entire period of the product’s life in order to increase resource-use efficiency and decrease liabilities; commonly referred to as “cradle-to-grave” analysis.
N
Natural Capital - A company’s environmental assets and natural resources existing in the physical environment, either owned (such as mineral, forest, or energy resources) or simply utilized in business operations (such as clean water and atmosphere).
Non-Governmental Organization (NGO) - A private, non-profit organization that is independent of business and government, that works toward some specific social, environmental, or economic goal through research, activism, training, promotion, advocacy, lobbying, community service, etc.
O
Open-Loop Recycling - A recycling process in which materials from old products are made into new products in a manner that changes the inherent properties of the materials.
Organic - A term signifying the absence of pesticides, hormones, synthetic fertilizers and other toxic materials in the cultivation of agricultural products; “organic” is also a food labeling term that denotes the product was produced under the authority of the Organic Foods Production Act.
S
Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) - An investment practice that gives preference to companies that value social and environmental impacts in addition to financial gain.
Sustainability - The successful meeting of present social, economic, and environmental needs without compromising the ability of future generation to meet their own needs; derived from the most common definition of sustainability, created in 1987 at the World Commission on Environment and Development.
Sustainable Design - A process of product, service, or organizational design that complies with the principles of social, economic, and environmental sustainability.
Sustainable Development - Development that utilizes tools, supplies and strategies that protect and enhance the earth’s natural resources and diverse eco-systems so as to meet the social and economic needs of the present without compromising the ability to meet the needs of the future.
T
Toxic Substances Control Act - This Act gives EPA the authority to require companies to report and keep records of the hazardous substances that they use. It also sets testing requirements on certain hazardous chemicals and restrictions on use of certain hazardous chemicals.
Transparency - A measure of increased accountability and decreased corruption in which a business reports on its ethics and performance results through accessible publication of the business’ practices and behavior.
Triple Bottom Line - A phrase describing a company’s improved top line financial performance over the long term due to sustainable business practices, including less capital investment and increased revenues. The triple bottom line refers to environmental, social, and economic sustainability.
W
Waste-to-Energy - A recovery process in which waste is incinerated or otherwise turned into steam or electricity, and used to generate heat, light or power through the process of combustion.
Waste-to-Profit - The process of using one company’s waste or byproduct as the input or raw material for another company, thereby increasing business profits and decreasing waste; also referred to as “byproduct synergy.”
Toolkit Navigation
- Contents & Acknowledgements
- Executive Summary
- Chapter 1: Why Lean and Six Sigma Are Important to the Environment
- Chapter 2: What Is Lean?
- Chapter 3: What Is Six Sigma?
- Chapter 4: How Do Lean and Six Sigma Relate to the Environment?
- Chapter 5: Why Does It Matter How We Talk About Lean and Environment?
- Chapter 6: Lean and Environment Applications
- Chapter 7: Conclusion
- Appendix A: Lean and Six Sigma Resources
- Appendix B: Lean and Environment Resources
- Appendix C: Lean and Six Sigma Glossary
- Appendix D: Environmental Glossary
- Appendix E: Summary of the Washington Lean and Environment Pilot Projects