Class VI - Wells used for Geologic Sequestration of CO2
On this page:
- Definition of Class VI wells
- Protecting drinking water resources
- Requirements for Class VI wells
- Background information about geologic sequestration
- Class VI guidance documents
- Geological Sequestration Data Tool
- Additional information
Definition of Class VI wells
Class VI wells are used to inject carbon dioxide (CO2) into deep rock formations. This long-term underground storage is called geologic sequestration (GS). Geologic sequestration refers to technologies to reduce CO2 emissions to the atmosphere and mitigate climate change.
Protecting drinking water resources
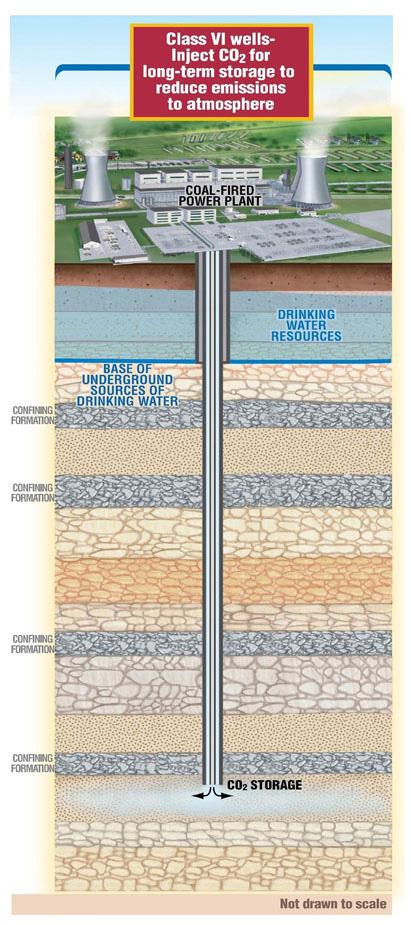 UIC Class VI wells inject CO2 for long-term storage to reduce emissions to the atmosphere.Class VI well requirements are designed to protect underground sources of drinking water (USDWs). Requirements address:
UIC Class VI wells inject CO2 for long-term storage to reduce emissions to the atmosphere.Class VI well requirements are designed to protect underground sources of drinking water (USDWs). Requirements address:
- Siting
- Construction
- Operation
- Testing
- Monitoring
- Closure
The regulations address the unique nature of CO2 injection for GS, including the:
- Relative buoyancy of CO2
- Subsurface mobility
- Corrosivity in the presence of water
- Large injection volumes anticipated at GS projects
In December 2010, EPA published the Federal Requirements Under the Underground Injection Control (UIC) Program for Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Geologic Sequestration (GS) Wells Final Rule (Class VI Rule).
Review the Final Rule for Class VI wells.
Requirements for Class VI wells
EPA developed specific criteria for Class VI wells:
- Extensive site characterization requirements
- Injection well construction requirements for materials that are compatible with and can withstand contact with CO2 over the life of a GS project
- Injection well operation requirements
- Comprehensive monitoring requirements that address all aspects of well integrity, CO2 injection and storage, and ground water quality during the injection operation and the post-injection site care period
- Financial responsibility requirements assuring the availability of funds for the life of a GS project (including post-injection site care and emergency response)
- Reporting and recordkeeping requirements that provide project-specific information to continually evaluate Class VI operations and confirm USDW protection
Background information about geologic sequestration
Geologic sequestration is the process of injecting carbon dioxide, captured from an industrial (e.g., steel and cement production) or energy-related source (e.g., a power plant or natural gas processing facility), into deep subsurface rock formations for long-term storage. This is part of a process frequently referred to as “carbon capture and storage” or CCS.
Underground injection of CO2 for purposes such as enhanced oil recovery (EOR) and enhanced gas recovery (EGR) is a long-standing practice. CO2 injection specifically for GS involves different technical issues and potentially much larger volumes of CO2 and larger scale projects than in the past.
EPA has finalized requirements for GS, including the development of a new class of wells, Class VI, under the authority of the SDWA's UIC program. These requirements, also known as the Class VI rule, are designed to protect underground sources of drinking water.
The Class VI rule builds on existing UIC program requirements, with extensive tailored requirements that address carbon dioxide injection for long-term storage to ensure that wells used for geologic sequestration are appropriately:
- Sited
- Constructed
- Tested
- Monitored
- Funded and closed
The rule provides owners or operators injection depth flexibility in different geologic settings across the United States. The flexibility includes deep formations and oil and gas fields transitioned to carbon dioxide storage sites.
In a separate rulemaking under authority of the Clean Air Act, EPA has finalized reporting requirements under the Greenhouse Gas Reporting program for all facilities that inject CO2 underground. Information obtained under the Greenhouse Gas Reporting program will enable EPA to track the amount of carbon dioxide received by these facilities.
Class VI guidance documents
EPA developed guidance documents to support the Class VI regulations. The guidance documents were prepared to provide program implementation assistance for UIC directors and compliance assistance for owners or operators of Class VI wells. The final guidance documents clarify the requirements of the Class VI regulations and provide additional recommendations for implementation and compliance.
Review Class VI guidance documents.
Geological Sequestration Data Tool (GSDT)
Under the Class VI Rule at 40 CFR 146.91(e), owners or operators of Class VI wells must submit geologic sequestration (GS) project information directly to EPA in an electronic format approved by EPA. This requirement applies regardless of whether the project is located in a state with primary enforcement authority (primacy) for Class VI wells.
EPA’s Geologic Sequestration Data Tool (GSDT) is a centralized, web-based system that receives, stores, and manages Class VI data and satisfies the Class VI electronic reporting requirement. Operators applying for Class VI Permits in states where EPA has direct implementation authority must submit application materials to EPA via the GSDT. Permit applicants can download a GSDT Registration Form on the system login page at https://epa.velo.pnnl.gov/ .
See the resources below for additional information on the GSDT, Class VI data management, and reporting.
Resources
Additional information
Additional information on climate change and sequestration can be found at EPA’s Global Warming and the Department of Energy websites.
Additional information on supporting documents relating to the development of the GS rule can be found at Regulations.gov.
