Aluminum Forming Effluent Guidelines
 EPA promulgated the Aluminum Forming Effluent Guidelines and Standards (40 CFR Part 467) in 1983 and amended the regulation in 1988. The regulation covers direct and indirect dischargers. The Effluent Guidelines and Standards are incorporated into NPDES permits for direct dischargers
EPA promulgated the Aluminum Forming Effluent Guidelines and Standards (40 CFR Part 467) in 1983 and amended the regulation in 1988. The regulation covers direct and indirect dischargers. The Effluent Guidelines and Standards are incorporated into NPDES permits for direct dischargers![]() direct dischargerA point source that discharges pollutants to waters of the United States, such as streams, lakes, or oceans., and permits or other control mechanisms for indirect dischargers
direct dischargerA point source that discharges pollutants to waters of the United States, such as streams, lakes, or oceans., and permits or other control mechanisms for indirect dischargers![]() indirect dischargerA facility that discharges pollutants to a publicly owned treatment works (municipal sewage treatment plant). (see Pretreatment Program).
indirect dischargerA facility that discharges pollutants to a publicly owned treatment works (municipal sewage treatment plant). (see Pretreatment Program).
- What is the Aluminum Forming Industry?
- Facilities Covered
- Guidance Documents
- Rulemaking History
- Additional Information
What is the Aluminum Forming Industry?
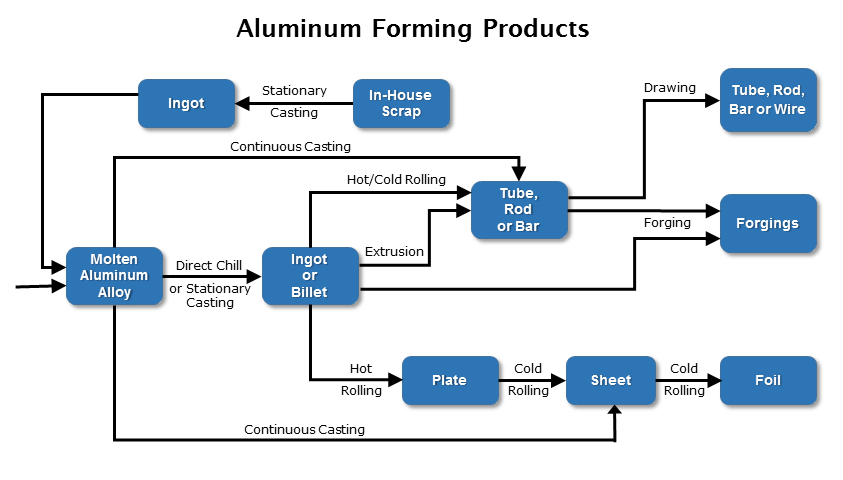
Aluminum forming is the deformation of aluminum or alloys into specific shapes by hot or cold working such as rolling, extrusion, forging, and drawing. Also included are a number of ancillary operations such as casting, heat treatment, and surface treatment that are an integral part of aluminum forming processes and that can contribute significantly to the wastewater discharged from aluminum forming plants.
- Cast ingots and billets are the starting point for making sheet and plate, extrusions, and forgings, as well as rod and wire.
- Rolled aluminum sheet and plate can be used as stock for stampings, can blanks, and roll formed products; as finished products in building, ship and aircraft construction; or as foil.
- Extrusions can be used as raw stock for forging and drawing; to fabricate final products, such as bumpers, window frames, or light standards; or can be sold as final products, such as beams or extruded tubing.
- Forgings are either sold as consumer products or used as parts in the production of machinery, aircraft, and engines.
- 331315: Aluminum Sheet, Plate, and Foil Manufacturing
- 331316: Aluminum Extruded Product Manufacturing
- 331319: Other Aluminum Rolling and Drawing
- 332112: Nonferrous Forging
Facilities Covered
The Aluminum Forming regulation is organized into six subcategories. Each subcategory consists of core and ancillary operations. The core operations include the forming operation along with processes that are either closely linked with that forming operation or generate very little or no wastewater. Some plants are covered by more than one subcategory.
- Rolling With Neat Oils
- Rolling With Emulsions
- Extrusion
- Forging
- Drawing With Neat Oils
- Drawing With Emulsions or Soaps
Clarification on the Applicability Statement
-
Paragraph (a) is a broad description of those facilities covered by this rule.
-
Paragraph (b) says that all aluminum forming facilities as described in the first paragraph are covered by the rule, except for “plants identified under paragraph (c).”
-
Paragraph (c) provides that indirect discharging small extrusion and small drawing with emulsions or soaps facilities
 Small extrusion and small drawing with emulsions or soaps facilitiesExtrusion facilities that extrude less than 3 million pounds of product per year and draw with emulsions or soaps less than 1 million pounds per year [40 CFR 467.01(c)] are covered by the rule. In fact, contrary to the language of paragraph (b), paragraph (c) does not identify any facilities that are not subject to the rule.
Small extrusion and small drawing with emulsions or soaps facilitiesExtrusion facilities that extrude less than 3 million pounds of product per year and draw with emulsions or soaps less than 1 million pounds per year [40 CFR 467.01(c)] are covered by the rule. In fact, contrary to the language of paragraph (b), paragraph (c) does not identify any facilities that are not subject to the rule.
In other words, all facilities that meet the description of the first paragraph, regardless of their size or how they form the aluminum, are covered by this regulation.
| Unit Operation | Wastestream |
|---|---|
| Annealing | Atmosphere scrubber liquor |
| Artificial aging | (Dry operation) |
| Cleaning, etching, or other surface treatment | Bath: caustic, acid, seal, or detergent solutions; rinse water; scrubber liquor |
| Cold rolling | Spent neat oil or emulsion |
| Continuous rod casting | Spent lubricant, contact cooling water |
| Continuous sheet casting | Spent lubricant |
| Degassing | Scrubber liquor |
| Direct chill casting | Contact cooling water |
| Drawing | Spent neat oil, emulsion, or soap solution |
| Extrusion die cleaning | Bath caustic solution, rinse water, scrubber liquor |
| Extrusion dummy block cooling | Contact cooling water |
| Forging | Scrubber liquor |
| Homogenizing | (Dry operation) |
| Hot rolling | Spent emulsion |
| Press heat treatment | Contact cooling water |
| Roll grinding | Spent emulsion |
| Sawing | Spent neat oil or emulsion |
| Solution heat treatment | Contact cooling water |
| Solvent degreasing | Spent solvents |
| Stationary casting | (Dry operation) |
| Swaging | (Dry operation) |
* For the complete list of processes and wastestreams see the regulation at 40 CFR Part 467
Surface Treatment
For the purposes of this regulation, surface treatment is considered to be a part of the Aluminum Forming Category whenever it is performed as an integral part of aluminum forming. All surface treatment of aluminum is considered to be an integral part of Aluminum Forming whenever it is performed at the same plant site at which aluminum is formed, and such operations are not considered for regulation under the Electroplating (40 CFR Part 413) or Metal Finishing (40 CFR Part 433) categories.
Casting
Casting done at a plant which manufactures aluminum and also does aluminum forming is subject to the casting limitations for the aluminum manufacturing subcategories of the Nonferrous Metals Manufacturing Category (40 CFR Part 421), if there is no cooling of the aluminum prior to casting. If the aluminum is a remelted primary aluminum product and is cast at a facility for subsequent forming of aluminum, then the casting of remelted aluminum is subject to the Aluminum Forming Category limitations. Other aluminum casting operations are subject to the Metal Molding and Casting (Foundries) Category (40 CFR Part 464).
Other Related Categories
- Coil Coating (40 CFR Part 465)
- Metal Products and Machinery (40 CFR Part 438)
- Nonferrous Metals Forming and Metal Powders (40 CFR Part 471) - Manufacture of aluminum powders and the forming of parts from aluminum or aluminum alloy powders
Guidance Documents
- Aluminum, Copper, and Nonferrous Metals Forming and And Metal Powders Pretreatment Standards: A Guidance Manual (December 1989)
Guidance to publicly owned treatment works (POTWs) on the implementation and enforcement of categorical pretreatment standards. Includes a summary of wastewater treatment technologies used by the industry. - Guidance Manual for Implementing Total Toxic Organics (TTO) Pretreatment Standards (September 1985)
Rulemaking History
1988 Amendment
- Documents, including:
- Final rule (December 27, 1988)
- Proposed rule (March 19, 1986)
1983 Initial Rulemaking
- Documents, including:
- Final rule (October 24, 1983)
- Development Document (June 1984)
Industry description, wastewater characterization, treatment technologies, regulatory compliance cost estimates and pollutant loadings for the final rule - Proposed rule (November 22, 1982)
Additional Information
For additional information regarding Aluminum Forming Effluent Guidelines, please contact Samantha Lewis (lewis.samantha@epa.gov) or 202-566-1058.