Nonferrous Metals Forming and Metal Powders Effluent Guidelines
 EPA promulgated the Nonferrous Metals Forming and Metal Powders Category regulation (NFMF) (40 CFR Part 471) in 1985 and amended the regulation in 1989. The regulation covers direct and indirect dischargers. The Effluent Guidelines and Standards are incorporated into NPDES permits for direct dischargers
EPA promulgated the Nonferrous Metals Forming and Metal Powders Category regulation (NFMF) (40 CFR Part 471) in 1985 and amended the regulation in 1989. The regulation covers direct and indirect dischargers. The Effluent Guidelines and Standards are incorporated into NPDES permits for direct dischargers![]() direct dischargerA point source that discharges pollutants to waters of the United States, such as streams, lakes, or oceans., and permits or other control mechanisms for indirect dischargers
direct dischargerA point source that discharges pollutants to waters of the United States, such as streams, lakes, or oceans., and permits or other control mechanisms for indirect dischargers![]() indirect dischargerA facility that discharges pollutants to a publicly owned treatment works (municipal sewage treatment plant). (see Pretreatment Program).
indirect dischargerA facility that discharges pollutants to a publicly owned treatment works (municipal sewage treatment plant). (see Pretreatment Program).
- What is the Nonferrous Metals Forming and Metal Powders Industry?
- Facilities Covered
- Relationship to Other Categories
- Guidance Documents
- Rulemaking History
- Additional Information
What is the Nonferrous Metals Forming and Metal Powders Industry?
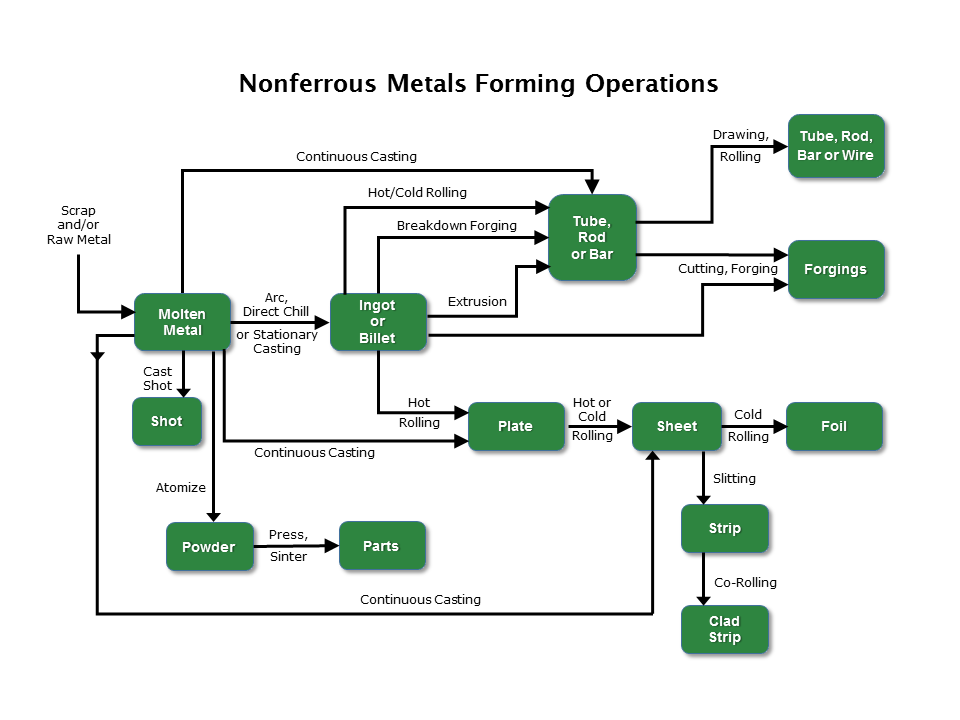
- Forming operations include rolling (both hot and cold), extruding, forging, and drawing; also cladding, tube reducing, swaging, and metal powder production.
- Ancillary operations include casting for subsequent forming, heat treatment, surface treatment, surface coating, alkaline cleaning, solvent degreasing, product testing, and wet air pollution controls on forming operations and the associated operations.
- Cast ingots and billets are the starting point for making sheet and plate, extrusions, and forgings, as well as rod, for use in drawing operations.
- Rolled sheet and plate can be used as stock for stampings, can blanks, and roll formed products; as finished products in building, and aircraft construction; or as foil.
- Extrusions can be used as raw stock for forging and drawing; or can be sold as final products, such as beams or extruded tubing.
- Forgings are either sold as consumer products or used as parts in the production of machinery, aircraft, and engines.
-
Nonferrous metal is defined as any pure metal other than iron, copper, or aluminum; or metal alloy for which a metal other than iron, copper, or aluminum is its major constituent by weight.
-
Alloys are considered as only one metal type. The metal type of any particular alloy is defined to be the metal that is the major component in percent by weight except for precious metals (silver, gold, platinum, and palladium) and beryllium. Any alloy containing 30 or greater percent by weight of precious metals is considered a precious metal alloy. Beryllium alloys are any alloy in which beryllium is present at 0.1 percent or greater by weight. Alloys for which iron, copper, or aluminum is greater than 50 percent by weight (except precious metals) are not included in the category of nonferrous metal alloys.
-
Metal powders include nonferrous metals and alloys as previously described, along with iron, copper, and aluminum and their alloys. Metal powder production processes include milling, abrading or atomizing.
-
The production of metal powders by chemical means, such as precipitation
-
The production of metal powder as the final step in refining metal
-
Forming of the metals beryllium, cadmium, chromium, gallium, germanium, indium, lithium, manganese, neodymium, or praseodymium.
-
331491: Nonferrous Metal (except Copper and Aluminum) Rolling, Drawing, and Extruding
-
332112: Nonferrous Forging
-
332999: All Other Miscellaneous Fabricated Metal Product Manufacturing
Note: The NAICS listing is provided as a guide and does not define the coverage of the NFMF category. For precise definitions of coverage, see the Applicability section at 40 CFR 471.01.
Facilities Covered
-
Lead-Tin-Bismuth Forming
-
Magnesium Forming
-
Nickel-Cobalt Forming
-
Precious Metals Forming
-
Refractory Metals Forming
-
Titanium Forming
- Uranium Forming
- Zinc Forming
- Zirconium-Hafnium Forming
- Metal Powders
Metal types covered
- Bismuth
- Cobalt
- Niobium (Columbium)
- Gold
- Hafnium
- Lead
- Magnesium
- Molybdenum
- Nickel
- Palladium
- Platinum
- Rhenium
- Silver
- Tantalum
- Tin
- Titanium
- Tungsten
- Uranium
- Vanadium
- Zinc
- Zirconium
- Iron, Copper, and Aluminum Metal Powder Production and Powder Metallurgy Operations
Relationship to Other Categories
The production of metal powders by chemical means may be regulated under the Inorganic Chemicals Manufacturing Category (40 CFR Part 415). The production of metal powders as the final step in refining metal is regulated under the Nonferrous Metals Manufacturing Category (40 CFR Part 421).
-
Casting of parts is included in the Metal Molding and Casting Category (Foundries) (40 CFR Part 464).
-
Casting which is an integral part of a nonferrous metals smelting and refining operation is included in the Nonferrous Metals Manufacturing Category (40 CFR Part 421) as is the production of metal powder as the final step in refining metal.
-
Casting of lead which is subsequently rolled and fabricated into battery cases is regulated under both NFMF and the Battery Manufacturing Category (40 CFR Part 461). The limitations for the casting operation for lead are the same in each category.
Surface treatment of nonferrous metals includes any chemical or electrochemical treatment applied to the surface of the metal. This process is considered to be an integral part of the NFMF category whenever it is performed at the same plant site at which nonferrous metals are formed. Wastewater discharges covered by the NFMF category are not subject to the Electroplating Category (40 CFR Part 413) or the Metal Finishing Category (40 CFR Part 433).
Guidance Document
- Aluminum, Copper, and Nonferrous Metals Forming and Metal Powders Pretreatment Standards: A Guidance Manual (December 1989).
This manual provides guidance to publicly owned treatment works (POTWs) on the implementation and enforcement of categorical pretreatment standards.
Rulemaking History
1989 Amendment
-
Final Rule (March 17, 1989)
1985 Initial Rulemaking
- Documents, including:
- Final Rule (August 23, 1985)
- Development Document (September 1986)
Industry description, wastewater characterization, treatment technologies, regulatory compliance cost estimates and pollutant loadings for the final rule - Proposed Rule (March 5, 1984)
Additional Information
For additional information regarding the Nonferrous Metals Forming and Metal Powders Effluent Guidelines, please contact Anthony Tripp, tripp.anthony@epa.gov or 202-566-1419.