Causal Pathway
Concept
Causal Pathway: Steps in the pathways linking sources to the cause can serve as supplementary or surrogate indicators that the cause and the biological effect are likely to have co-occurred.
Examples
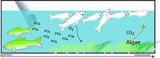
Consider low concentrations of dissolved oxygen as a candidate cause of decreased fish abundance. One of several causal pathways by which dissolved oxygen concentrations can be reduced is via an increase in nutrients allowing increased accumulation of algal biomass. When these algae eventually die, bacteria, fungi and protozoans can increase and rapidly consume the available oxygen. Given this causal pathway, what findings support or weaken the case for low levels of dissolved oxygen as the cause?
- Supporting evidence - Monitoring data show that sites with low fish abundance have higher nutrient concentrations or greater algal biomass than sites with high fish abundance.
- Weakening evidence - Monitoring data show that nutrient concentrations and algal growth measures are not higher at sites with reduced fish abundance, relative to unimpaired sites.
How Do I Analyze the Data?
Data relevant to the hypothesized steps linking a candidate cause to potential sources can be used to assess the likelihood that that agent is present. These steps in the causal pathway serve as surrogates for the proximate stressor when data on the stressor itself are unavailable or as supplementary sources of information when stressor data is available. Multiple causal pathways may lead to a candidate cause, and evidence supporting the steps in even one pathway can be enough to bolster the case for a candidate cause.
Candidate causes cannot be refuted using causal pathway evidence. Although some pathways may be eliminated, there are always potential unknown sources or pathways that may result in the candidate cause.
- Spatial/Temporal Co-occurrence
- Example analysis worksheet for Causal Pathway for the Little Scioto River, OH, USA
What Evidence Would Support or Weaken the Case for a Candidate Cause?
- Data showing that one or more steps in the causal pathways linking sources to the candidate cause are present at the impaired site, relative to unimpaired sites
- Data showing that one or more steps in the causal pathways linking sources to the candidate cause are not present at the impaired site, relative to unimpaired sites
How Do I Score the Evidence?
| Finding | Interpretation | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Data show that all steps in at least one causal pathway are present. | This finding strongly supports the case for the candidate cause, because it is improbable that all steps occurred by chance; it is not convincing because these steps may not be sufficient to generate sufficient levels of the cause. | ++ |
| Data show that some steps in at least one causal pathway are present. | This finding somewhat supports the case for the candidate cause. | + |
| Data show that the presence of all steps in the causal pathway is uncertain. | This finding neither supports nor weakens the case for the candidate cause. | 0 |
| AData show that there is at least one missing step in each causal pathway. | This finding somewhat weakens the case for the candidate cause, but is not strongly weakening because it may be due to temporal variability, problems in sampling or analysis, or unidentified alternative pathways. | - |
| Data show, with a high degree of certainty, that there is at least one missing step in each causal pathway. | This finding convincingly weakens the case for the candidate cause, assuming critical steps in each pathway are known, and are not found at the impaired site after a well-designed, well-performed, and sensitive study. | -- |
Helpful Tips
- Save data directly related to the proximate stressor for analysis under spatial/temporal co-occurrence or evidence of exposure or biological mechanism, as these types of evidence carry more weight.
- Causal pathway evidence considers the intermediate steps between sources and the proximate stressor, whereas evidence of exposure or biological mechanism considers the intermediate steps between the proximate stressor and the observed biological effect.
- Keep in mind that causal pathway evidence cannot refute the case for a candidate cause, because although critical steps in some pathways may appear to be absent, there may be unknown pathways or unknown system dynamics operating.